You might be planning to set up a physics lab for your school, college, research institution, or industry.
Before you set out to buy equipment and apparatus, you must have a rough idea of what your physics lab should look like.
This is called physics lab design. Read along to learn how to design your physics lab and set up your physics lab furniture.
Want us to do it for FREE? Head over here.
Physics Lab Design Layout
Before placing the furniture, you must first finalize the physics lab design. The design entirely depends on what you plan to do in the lab. Ask yourself:
- Are you planning to teach students the basics of hands-on physics?
- Are you setting up a high-end facility to test high-powered lasers?
- Are you conducting research experiments on semiconductors or states of matter?
Each type of lab requires different instrumentation, setup designs, and furniture. This, in turn, determines your physics lab layout.
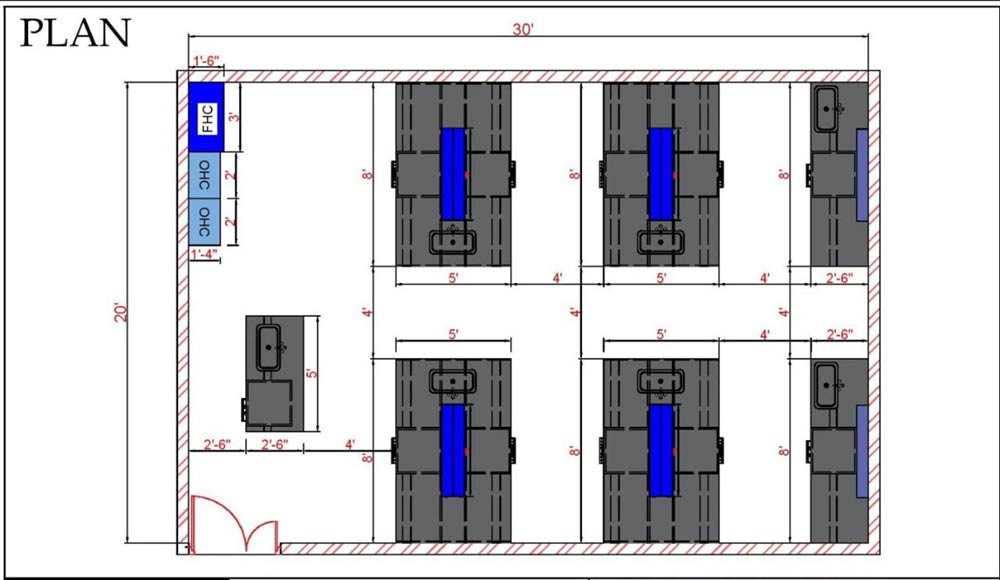
School Physics Labs
For school physics labs:
- Zone the lab into separate areas for experiments, demonstrations, and equipment storage.
- This zoning improves organization and minimizes congestion, thereby enhancing teaching efficiency.
- Ensure easy movement flow between workstations so instructors can monitor and guide students without causing interruptions.
- For CBSE-compliant senior secondary school physics labs, a minimum room size of 600 sq ft is recommended.
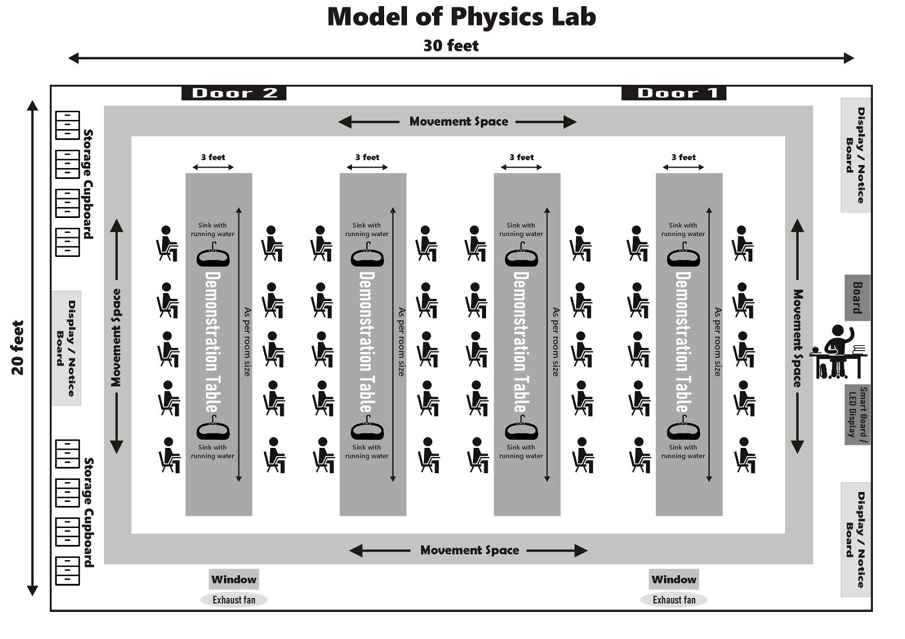
Physics Research Labs
Create dedicated zones for:
- Theoretical work
- Experimental setups
- Data analysis
For research labs zoning helps minimize distractions and improves workflow.
Open floor plans facilitate collaboration and allow flexible reorganization of equipment.
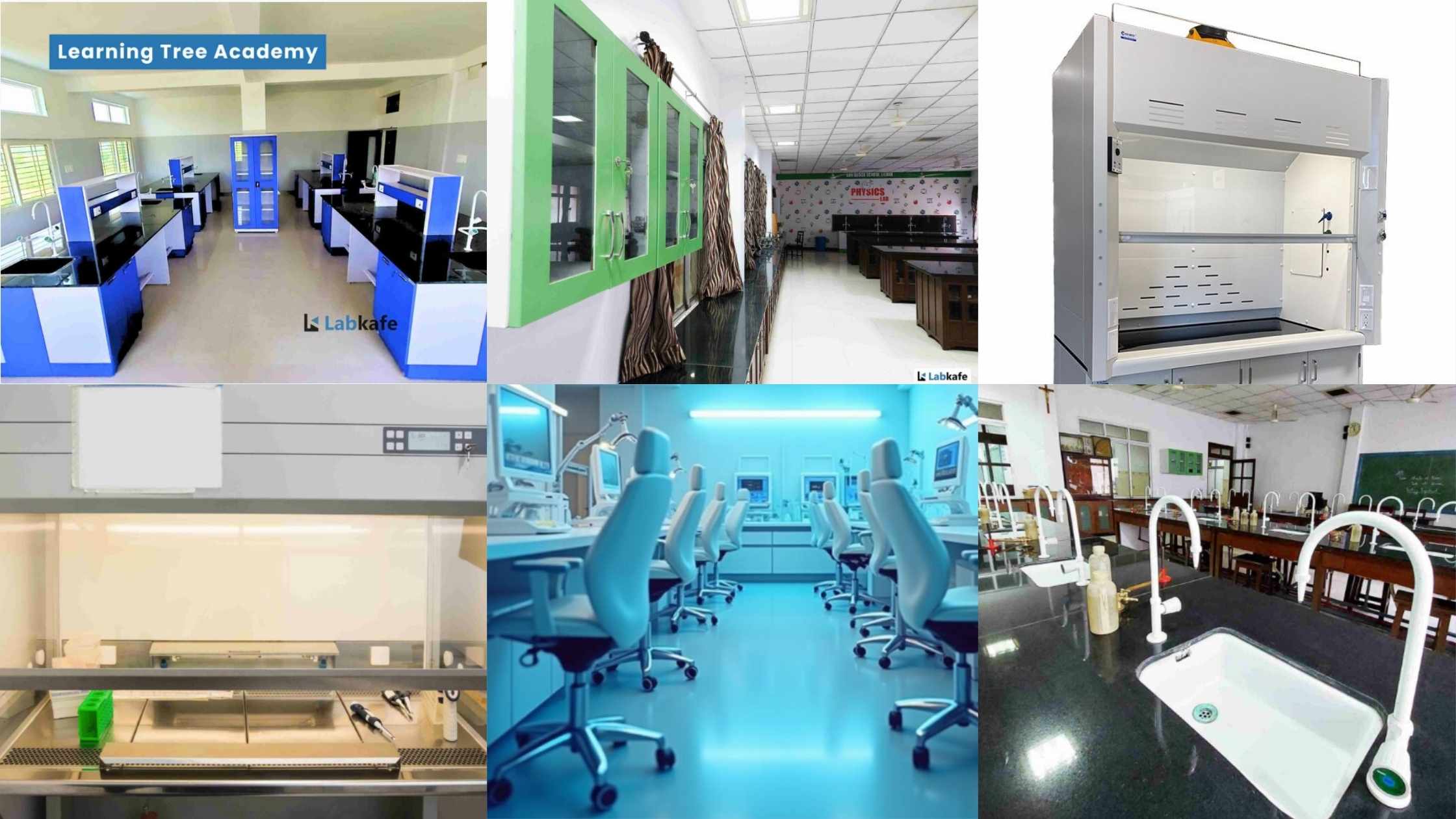
Lab Furniture and Ergonomics
Worktop and Storage Design
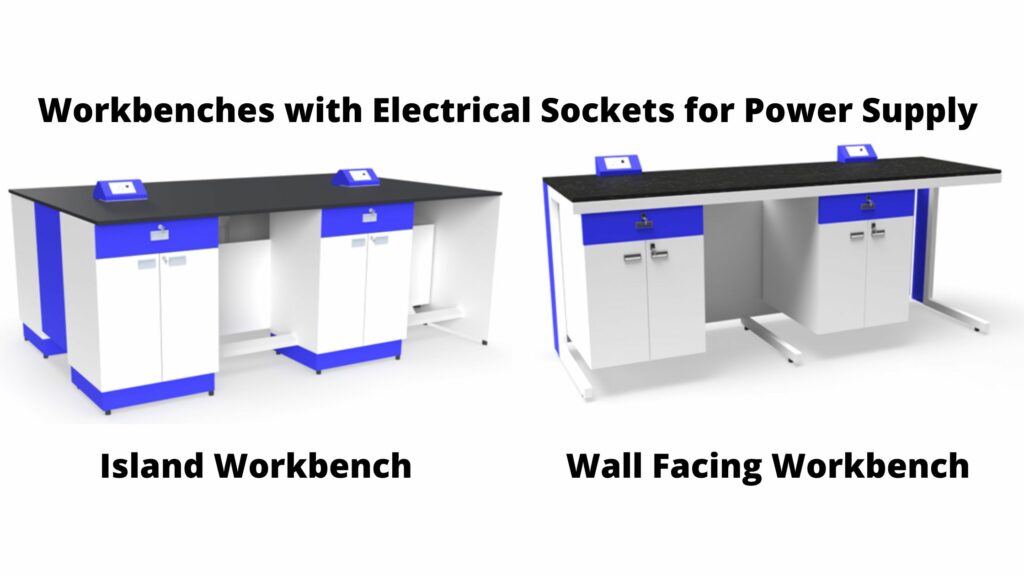
Physics worktops are the backbone of the lab, serving as the primary space for experiments and accommodating instruments and apparatus.
Under-bench cupboards and drawers are essential for keeping the workspace clear and providing easy access to equipment, often with locks for security. In teaching labs, benching is usually laid out facing the front of the classroom and the teacher’s space.
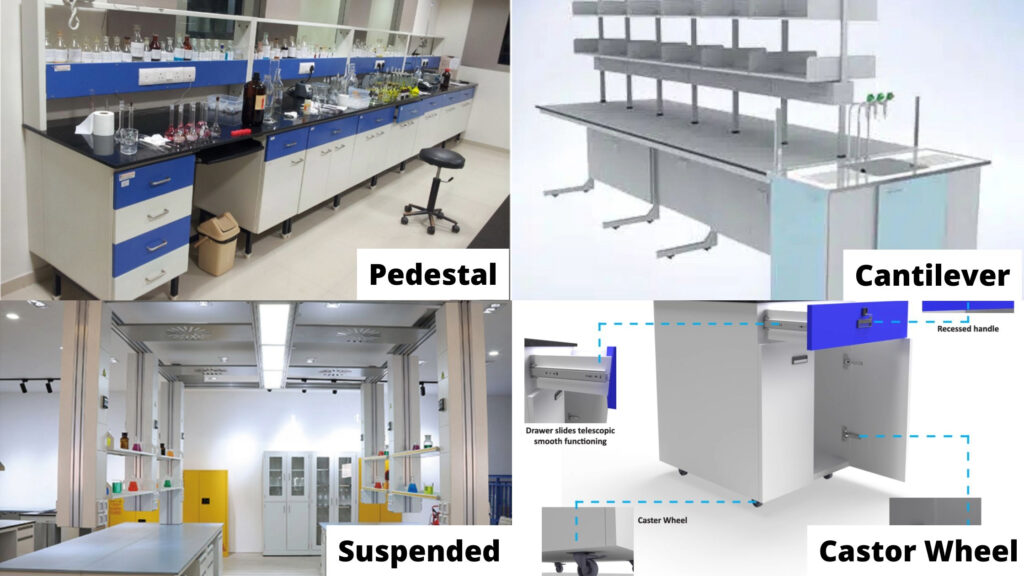
Several benching options are available:
- Pedestal: Worktops supported by cupboards.
- Cantilever: Supported by a framework with steel legs.
- Suspended: Allowing complete floor access for easy cleaning.
- Castor wheel: Wheels enable easy movement and floor cleaning.

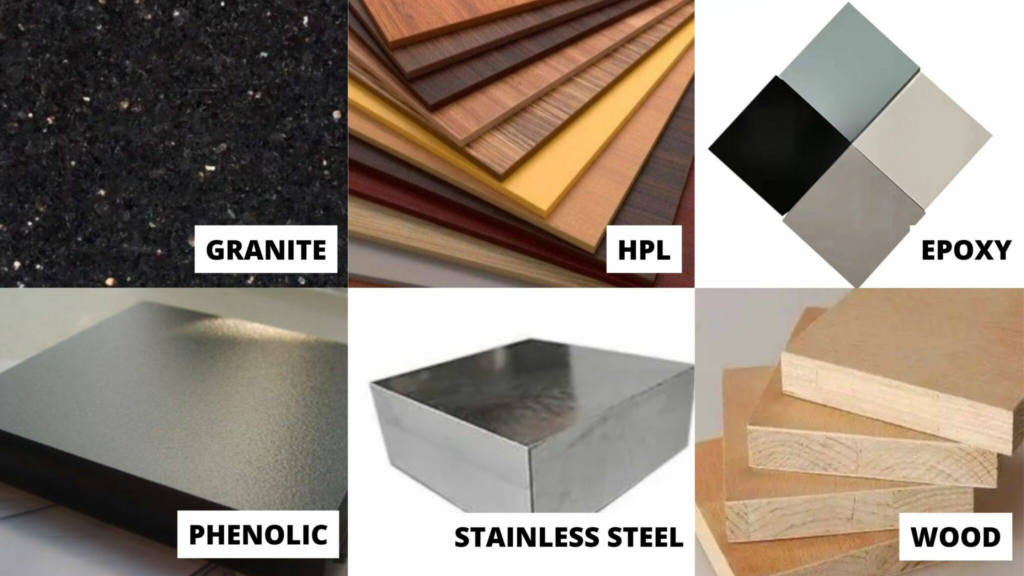
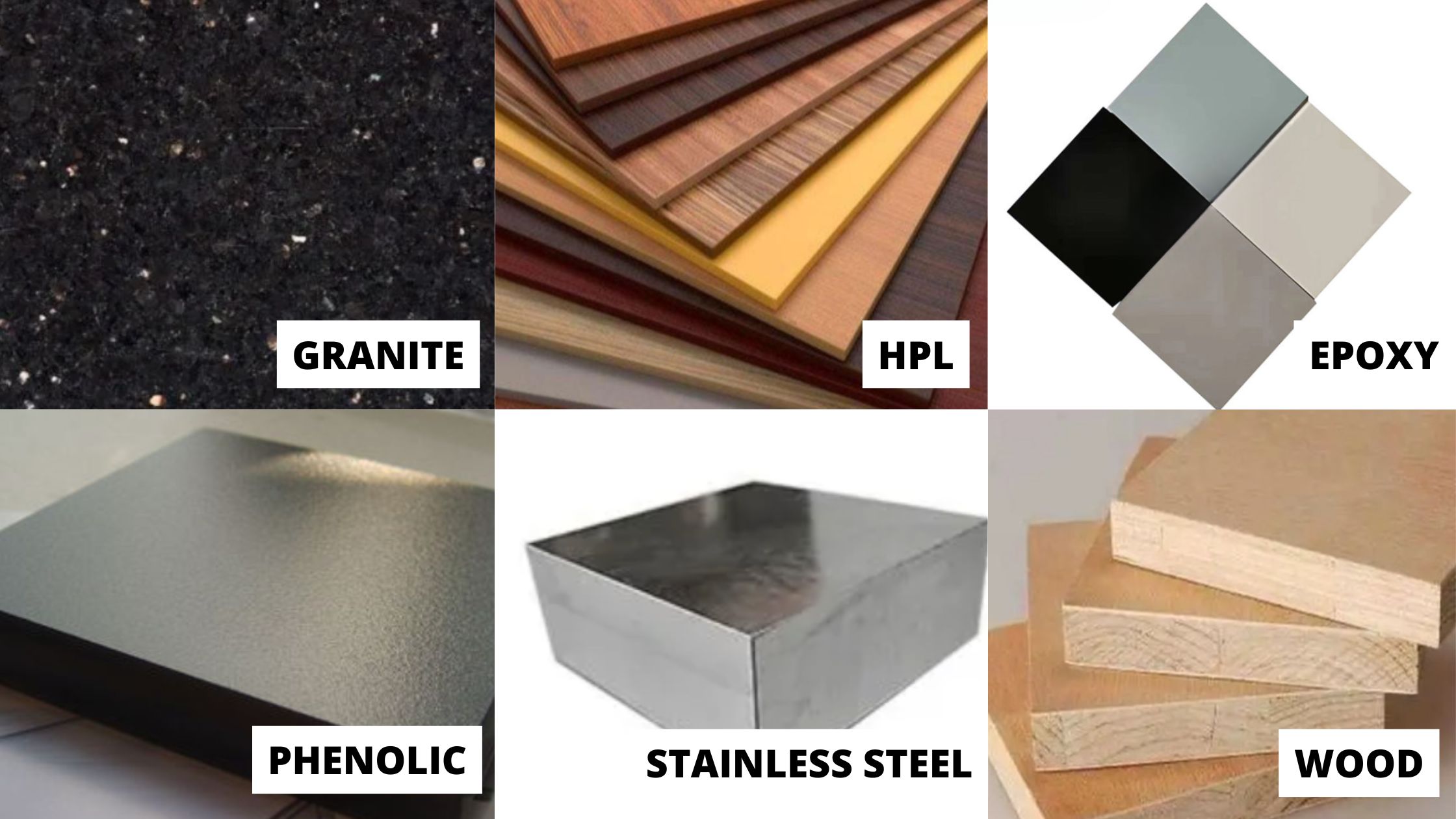
The type of work surface should also be chosen based on the intended use. For instance, Trespa work surfaces (solid grade laminate, acid-resistant) and epoxy resin sinks (resistant to mechanical and thermal shock) are suitable for physics labs.

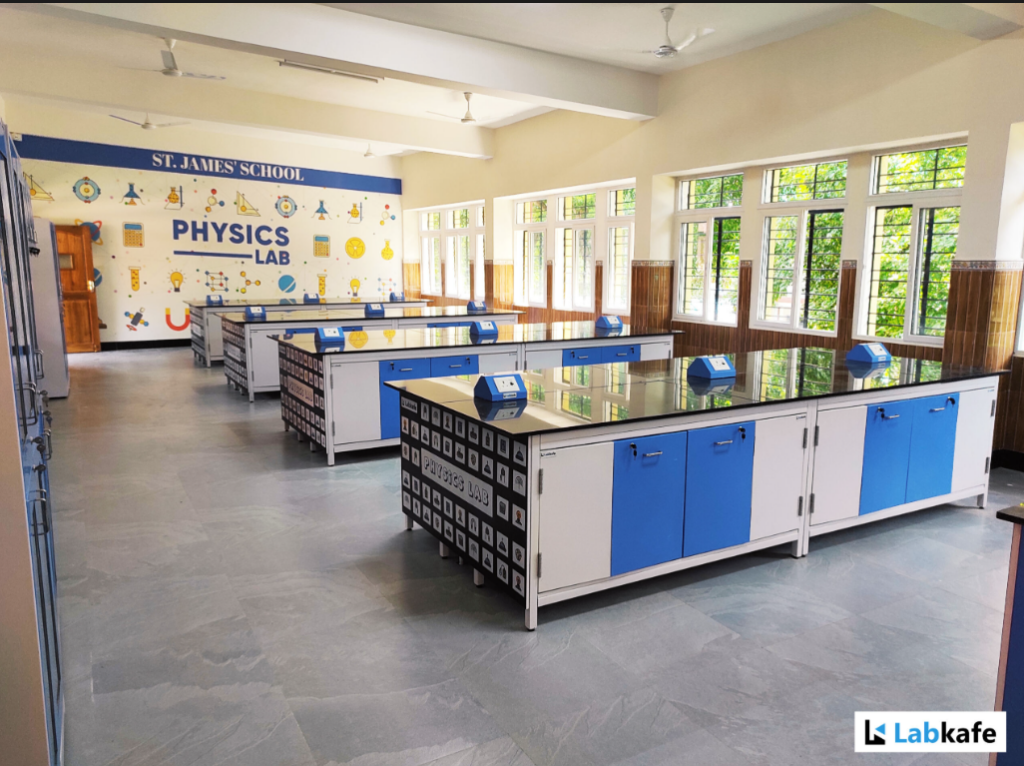
Comfort and Accessibility in Physics Lab Design
Ergonomics and comfort are important aspects of lab design. Key considerations include:
- Compliance with SEFA and BIFMA standards to ensure standard lab furniture quality
- Height-adjustable tables and chairs: Accommodate all students and reduce strain during extended lab sessions.
- Sufficient lighting: Ensure both general and task lighting at individual workstations to improve focus and accuracy.
- Accessibility features: Wide aisles for easy movement and adjustable workstations.
Physics Lab Equipment Placement and Storage Design
Careful placement of lab equipment is necessary for efficient workflow and safety. Secure consumables and non-consumables in a separate room or cupboard with a lock and key.
School Labs
- Store common tools like oscilloscopes, voltmeters, and power supplies accessibly.
- Group similar equipment in labeled cabinets to reduce search time.
Research Labs and Industries
- Use mobile workstations for flexibility when handling large equipment.
- Place hazardous equipment, such as lasers or high-voltage setups, in dedicated, well-marked areas with safety barriers and signage.
Colleges and Institutes
- Plan storage to accommodate large quantities of equipment needed for practical work.
- Secure consumables and non-consumables in a separate room or cupboard with a lock and key.
Electricity, Water, Gas, and Waste Disposal Facilities in Physics Lab Design
Electricity is an important resource in a physics lab. Depending on the experiments conducted, plan gas, water, and waste disposal facilities in different sections of the lab. Provide two separate bins for biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste.
Electricity
- Provide ample power outlets at each workstation.
- Install a breaker on each table for added safety.
- Integrate electrical power lines into table designs with student-safe sockets.
- Ensure electrical connections are easily accessible at every workstation for connecting instruments and apparatus.
Safety Considerations in Physics Lab Design
Safety is a top priority in physics lab design. Key safety measures include:
- Electrical Safety: Easily accessible circuit breakers, emergency shutoffs, and properly grounded outlets, especially near water sources.
- Laser Safety: Protective eyewear must be provided, and laser areas must be clearly marked with safety barriers.
- General Safety Protocols: Clearly marked emergency exits, accessible fire extinguishers, and first aid kits must be installed. Regular safety drills should be conducted.
Additionally, display a notice board with:
- Do’s and Don’ts
- Contingency measures
- Timetables
- Emergency contact numbers
Avoid touching equipment until instructed, never work without supervision, and ensure hands are dry when handling electrical components.
Incorporating Technology in Physics Lab Design
Modern physics research demands the integration of technology into the lab. Key elements include:
- Digital Tools: Equip the lab with digital sensors and data loggers to help students focus on data analysis.
- Interactive Learning: Install interactive smart boards or projectors to facilitate visual demonstrations.
- Computer Stations: Set up computer stations with physics simulation software, such as MATLAB, to enhance conceptual understanding.
Scalable Physics Lab Design

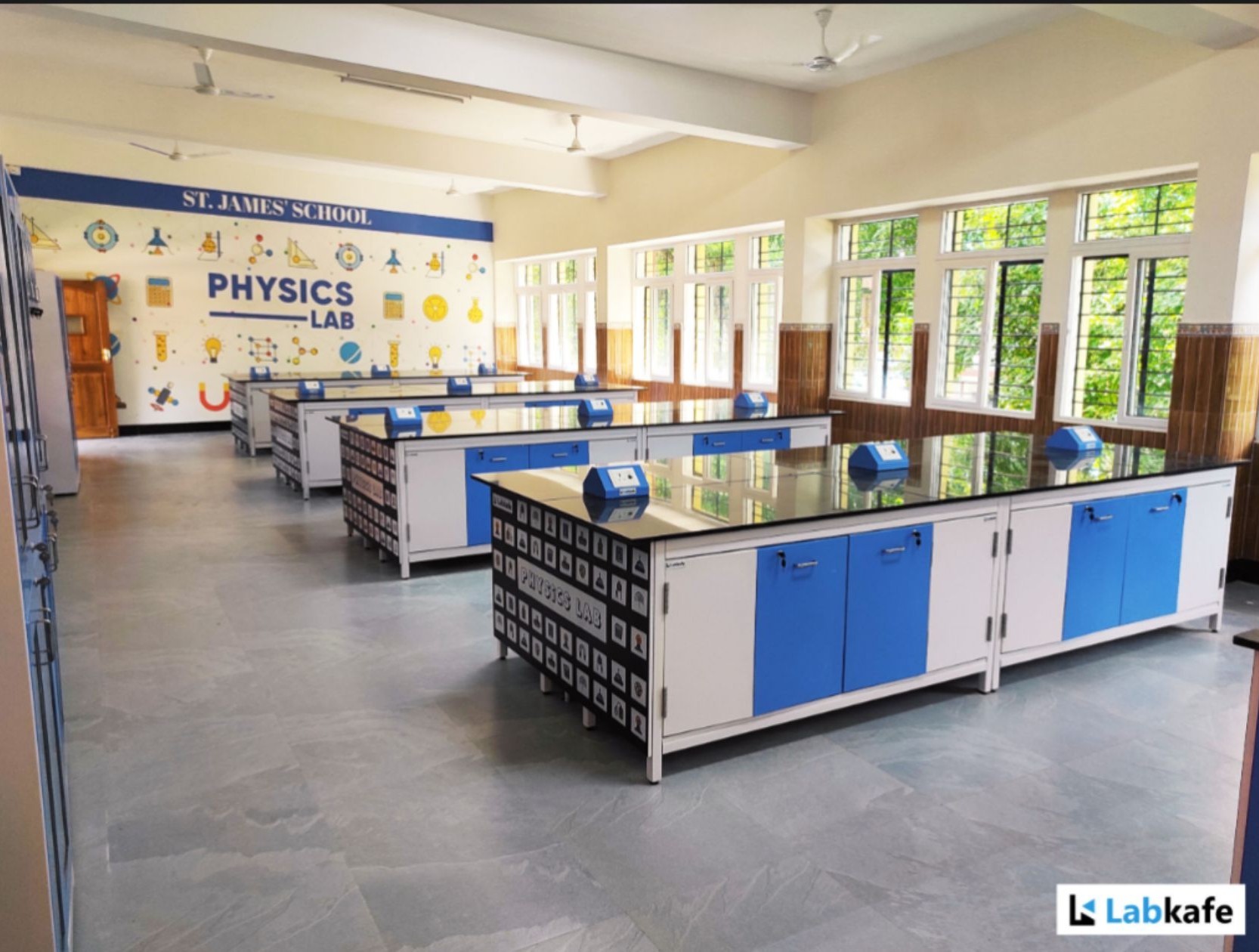
Designing a lab to accommodate future technological advancements and changing educational needs is essential.
Modular lab design, with reconfigurable workstations and shelving, allows easy adaptation for increased student volume once the school expands.
Planning for future equipment needs includes:
- Adequate electrical outlets
- Network connections
- Sufficient space for expansion
Lab systems like Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC), plumbing, and electrical services should be scalable to handle increased future demand.
Physics Lab Design and Furniture Budget
Budget considerations are important when designing a teaching lab.
Explore grants, CSR opportunities, and donation opportunities to cover initial setup costs or future expansions.
Conclusion
By carefully considering these factors, educators and designers can create physics labs that are not only functional and safe but also inspiring environments for learning and discovery.
Organizations like Labkafe offer specialized services in designing, manufacturing, supplying, and installing physics lab furniture tailored to specific needs for schools, colleges, research, and industry.
Want to explore a physics lab at home? Read more about the Physics Lab in a Box.
Perfect for schools (classes 6 to 10), busy homeschooling parents, and coaching institutes.












Leave a Reply