Wikipedia describes a typical workbench as “a table at which manual work is done”. It further explains how it could have a simple flat surface or a complex piece of design to get work done. Although as suggested earlier, workbench as a topic encompasses a very wide range of products and applications, in this blog we’ll restrict ourselves to workbenches related to laboratory and to be specific their tabletop materials.

As discussed earlier in our previous blog posts related to Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Composite laboratories, workbench requirement of each varies. While Chemistry and Biology deal with corrosive chemicals needing chemical resistant fireproof setup, Physics requires a more sturdy scratch proof setup. Similarly, Chemistry and Biology lab needs reagent racks to store glassware and chemicals for freeing up working table space and to prevent accidental spillage and breakage, Physics lab requires raceways for power sockets required in various experiments.
Before diving further into tabletop materials lets discuss some of the attributes of lab workbenches:
- Workbenches are mostly rectangular in shape, with the flat smoother surface with edge binding
- A standard height for comfortable usage predefined by age (as the height of school children and adult varies) and mode of working in sitting or standing position
- Provisions for storing extra equipment and easy access
- The work surface should be hygienic, easy to clean, chemical and stain resistance and should last long
Traditionally, workbenches were made of many different materials including metal, wood, stone, and composites depending on the requirements of the laboratory.
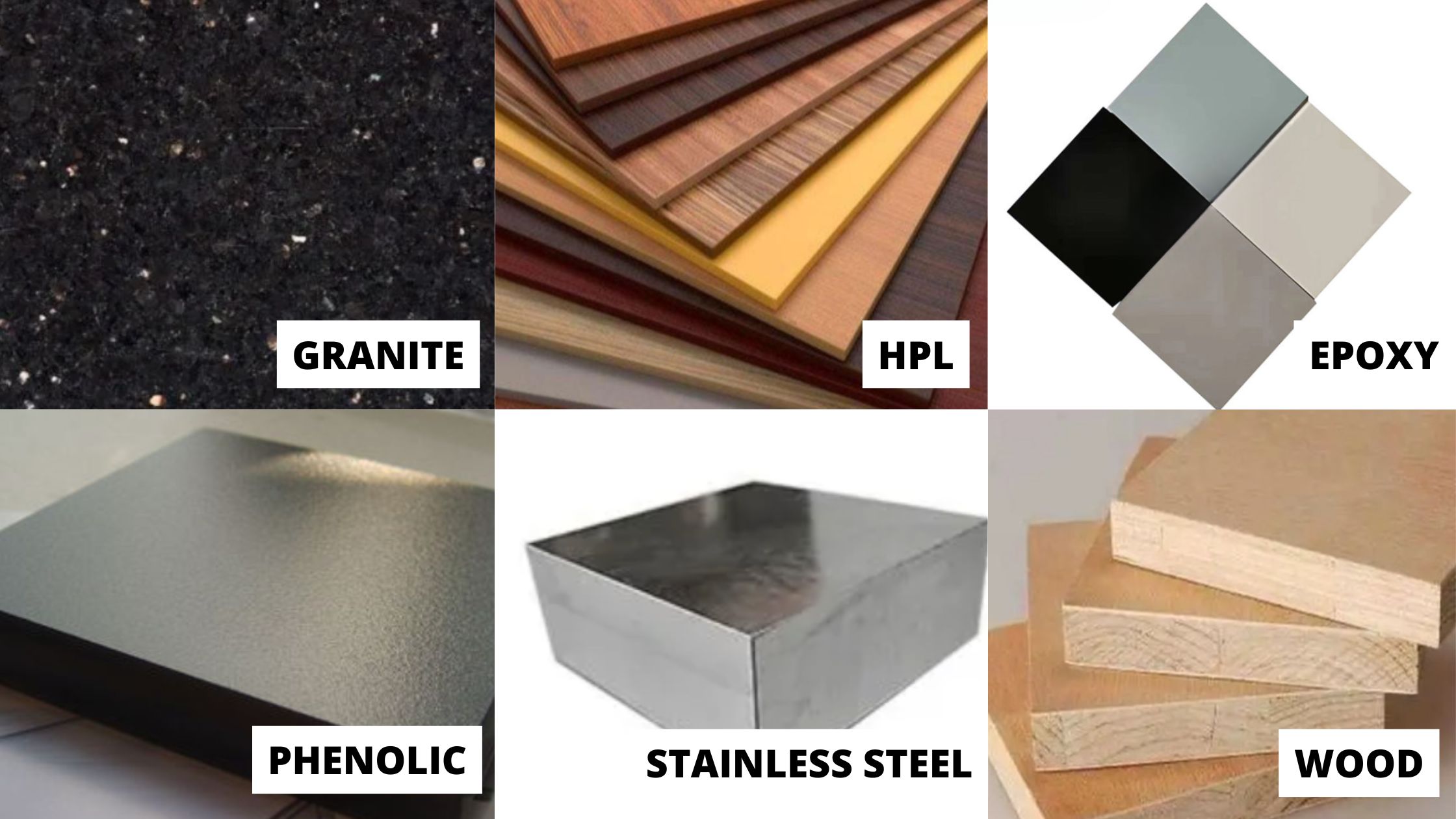
Following materials are generally preferred:
Medium-density fibreboard (MDF)
Medium-density fibreboard (MDF) is an engineered wood product. For making MDF board, hardwood/softwood particles are broken down into wood fibers then combined with adhesive material and are made into predetermined panels by applying high temperature and pressure. The composition varies depending upon the specification but on a standard level, it is typically made up of 82% wood fiber, 9% urea-formaldehyde resin glue, 8% water, and 1% paraffin wax. Due to subjected pressure and temperature, materials fuse and gets compressed resulting in a denser and stronger product as compared to plywood.

Advantages of MDF
- Isotropic in nature meaning its properties remain the same in all directions due to lack of grains
- Consistent in strength and size throughout its cross-section
- Shapes well and can be formed into desired shapes
- No expansion or contraction over time if sealed around edges
Ply Laminate
Ply Laminate is plywood with a laminate of a particular color or design pasted on top of it. Thin layers of wood mixed with adhesive are placed alongside & on top of each other keeping grain alignment in a particular direction. This assembly is then applied pressure via bench press to form sheets. The entire sheet has a grain alignment in a particular direction. Again these sheets are stacked with grains alignment is different directions along with a top layer of the laminate. The same process of applying adhesive and stress via bench press is repeated.

Advantages of Ply Laminate
- Moisture resistant
- Workable into desirable shapes
- Consistent in strength and size throughout the cross-section
- Chemical Resistant
- Durable
Granite
Granite has been a popular choice for countertop material. It is an igneous rock with a low level of permeability making it moisture resistant. It is nearly always massive, hard and tough, and therefore it has gained widespread use throughout human history as a construction stone. With a very high melting temperature of 650 degrees Celcius, it has excellent temperature resistant.

It is, however, prone to etching that is dulling of granite top surface due to reaction with acids.
Advantages of Granite
- Moisture resistant
- Consistent in strength and size throughout the cross-section
- Durable
- Excellent temperature resistance
Phenolic Plywood
A phenolic board is made by subjecting phenolic resins on plywood forming a glossy layer on the top resulting in higher strength than the base material. It is also resistant to water, chemical and scratch.
When Phenol (C2H5OH) is combined with Formaldehyde, it produces a phenolic resin.
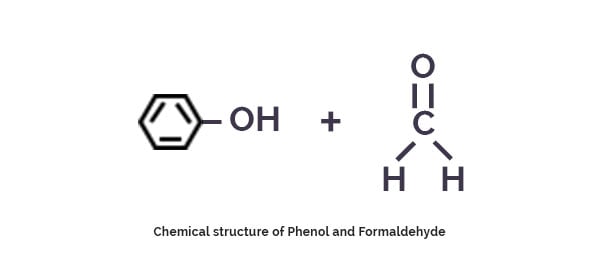
This resin is then used along with a sheet of paper to cover both sides of the desired plywood. Upon subjection to high temperature and pressure, phenolic resins act as thermosetting compound and get homogeneously reinforced with cellulose fibers of plywood to give Phenolic Boards. Upon subjection to heat and pressure, phenolic resin combines with cellulose fibers resulting in a smooth, glossy and very tough surface.

Advantages
- Higher level of chemical resistance
- Moisture resistant
- Shapes well and can be worked into desirable shapes
- Hygienic, odorless and easy to clean
- Consistent in strength and size throughout the cross-section
- Durable
You can read more about it here.
Epoxy Resins Board
An Epoxy Resins Board, used in making countertops, is made by subjecting epoxy resins on plywood (generally used but other materials can also be used). It forms a protective glossy layer on the top resulting in higher strength than the base material. Epoxy resins out-perform than most of the other resin types in terms of mechanical properties and resistance to environmental degradation. The finished surface provides a higher level of resistance to water degradation.

The term ‘epoxy‘ refers to a chemical group consisting of an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms that are already bonded in some way. The simplest epoxy is a three-member ring structure known by the term ‘alpha-epoxy’ or ‘1,2-epoxy’. The idealized chemical structure is shown in the figure below.
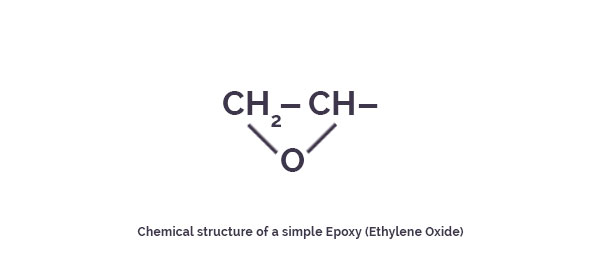
Both the liquid resin and the curing agents form low viscosity easily processed systems. Epoxy resins are easily and quickly cured at any temperature from 5°C to 150°C, depending on the choice of curing agent. One of the most advantageous properties of epoxies is their low shrinkage during cure which minimizes internal stresses and porosity resulting in improved moisture resistance. Epoxy resins are formed from a long chain molecular structure with epoxy groups as reactive sites at either end. The epoxy molecule also contains two ring groups at its center which are able to absorb both mechanical and thermal stresses better than linear groups and therefore give the epoxy resin very good stiffness, toughness and heat resistant properties. The figure below shows the idealized chemical structure of a typical epoxy.
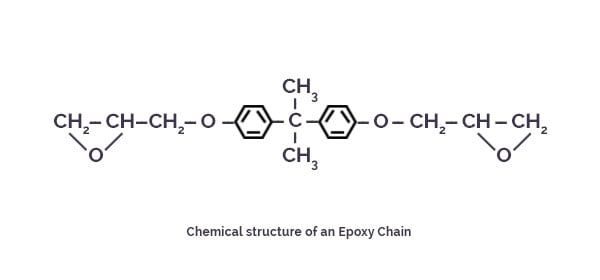
Epoxies differ from polyester resins in that they are cured by a ‘hardener’ rather than a catalyst. The hardener, often an amine, is used to cure the epoxy by an ‘addition reaction’ where both materials take place in the chemical reaction. The chemistry of this reaction means that there are usually two epoxy sites binding to each amine site. This forms a complex three-dimensional molecular structure. You can read more about it here.
Advantages of Epoxy Resins Board
- Zero VOC (Volatile Organic Content), which means no solvents or harmful odors to breathe
- Creates a lifetime seamless, hard and non-porous finish which eliminates staining
- No unsanitary joints or grout lines that can attract other microorganisms
- Rock hard, durable, scratch & impact resistant to 15,000 psi, five times stronger than concrete
- Thickness of 100 mils (2.54mm) or more, creating an extreme 3D effect
- Can be used on Plywood or MDF
Strength of countertop materials
Wood is made up of grains that develop in the direction of growth of the tree. These grains are tightly packed and the compactness directly affects the strength of any given wood type. Harwood is hard because of this grain compactness and so is the case with softwood. You can read about wood grains here.
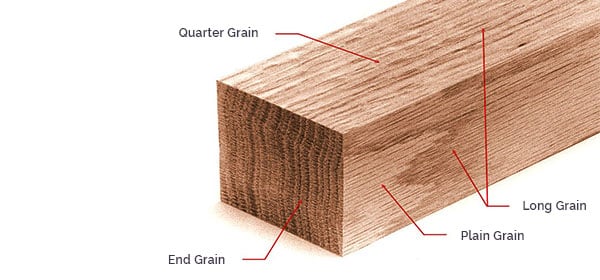
For a material to get deformed upon subjection of adequate stress, dislocation movement needs to be higher. During the course of making MDF or Plywood, boards are subjected to stress perpendicular to the surface. This increases the resistance of the board in that very direction by increasing dislocation density and grain boundary breakage. If, later on, the material is subjected to stress in this very direction then the board will be able to withstand it.

Property overview of countertop materials
Let us review what we discussed till now related to how manufacturing process and additives of each differs. Also how on properties front they all stand.
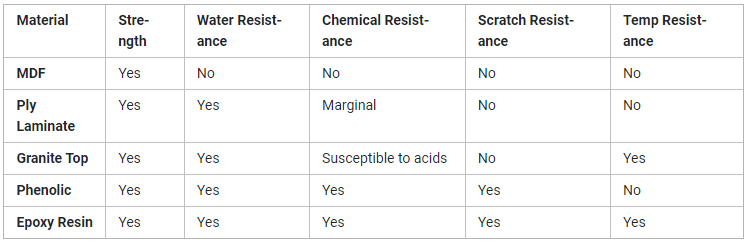
So, this was a in-depth overview of all the materials that are commonly used to make furniture with an emphasis on laboratory workbench and countertop.
At Labkafe, we provide laboratory furniture and equipment. In laboratory furniture, we first design the entire laboratory room keeping in mind the requirements. Also, we take care of the complete installation of laboratory furniture. In lab equipment section, we have a wide range of glassware, chemicals, equipment and other lab accessories. Most of them are available for order online from our website but some of them can be procured on demand. If you have any sort of laboratory requirements do mail us at [email protected] and we’ll get in touch with you. Also, you can download our Furniture and Laboratory Equipment catalog from here.












Leave a Reply