Category: How To Teach
-

Atmospheric Refraction: Definition, Causes, and Effects
What is Atmospheric Refraction? Atmospheric refraction refers to the bending of light as it travels through the Earth’s atmosphere. This occurs because the atmosphere consists of layers with varying optical densities due to differences in temperature and pressure. Light bends toward the normal when moving from a rarer to a denser layer. As light travels…
-

Autophagy- Fasting as an Inducer
What is autophagy? Just like our homes produce garbage, our body’s cells generate waste too. Similar to how garbage bins help clear waste from our homes, our cells have their own waste disposal system called autophagy. In this process, damaged components of the cell are broken down and recycled into useful by-products for the cell…
-

Pulley System for Load Distribution: Complete Explanation
What is a pulley? A pulley system uses an inextensible string. When one end of the string is pulled by 1 meter, the other end moves by the same distance. This demonstrates the concept of constrained motion or constrained length. Applying a force to one end of the string directly affects the motion at the…
-

Transformer Works on the Principle of Faraday’s Law of Mutual Electromagnetic Induction
A transformer works on the principle of Faraday’s Law of Mutual Electromagnetic Induction. Faraday’s first Law states that when a conductor is placed in a varying magnetic field, an electromotive force is induced. Let us understand how this phenomenon helps us increase and decrease the voltage in circuits using a transformer. This law is at…
-
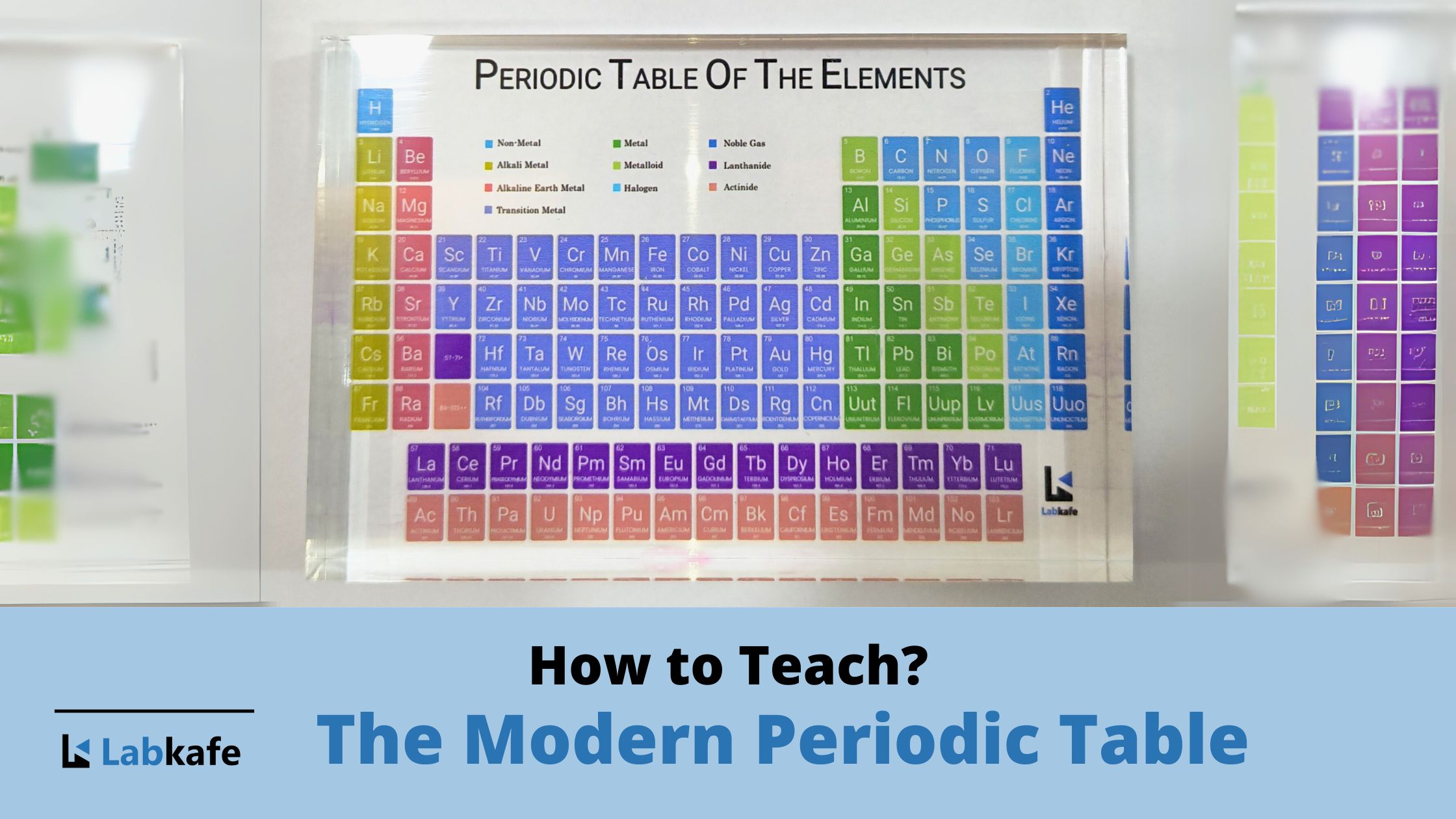
The Modern Periodic Table Chart
The Modern Periodic Table helps us predict the properties of elements based on their atomic number. Without this structure, identifying patterns in chemical behavior would be difficult and inconsistent. Earlier attempts to classify elements lacked a reliable basis, which made chemical trends harder to explain. Henry Moseley solved this in 1913 by organizing elements according…
-

What is Power of Hydrogen (pH)?
The power of hydrogen, or pH (also called the potential of hydrogen), measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. The formula for calculating the pH of a liquid is: pH = -log [H⁺] A higher pH indicates lower acidity and higher alkalinity in the solution. Conversely, a lower pH means higher acidity and…
-

How to Teach Kinetic and Potential Energy?
Energy as a function of work Kinetic and potential energy are a function of work. It is defined as the product of the force applied on a body and the displacement of the body caused by this force. Mathematically, it is expressed as: W = F × d where W represents work, F is force,…
-

How to Teach the Concept of a Coupled Pendulum?
What is a pendulum? A pendulum is a fascinating device that consists of a ball-shaped mass, known as the “bob,” suspended by a theoretically massless string from a fixed point. An extension of this is the coupled pendulum, which we shall study in a while. When you displace this bob from its starting position, it…
-

How to Teach Wave Motion and its Properties?
Waves aren’t always visible. When you drop a pebble in water, it may look like the water is flowing outward, but that’s not the case. To understand what’s happening, you need to understand waves. If you place a cork in the water and drop a pebble nearby, you’ll see the cork bobbing up and down.…