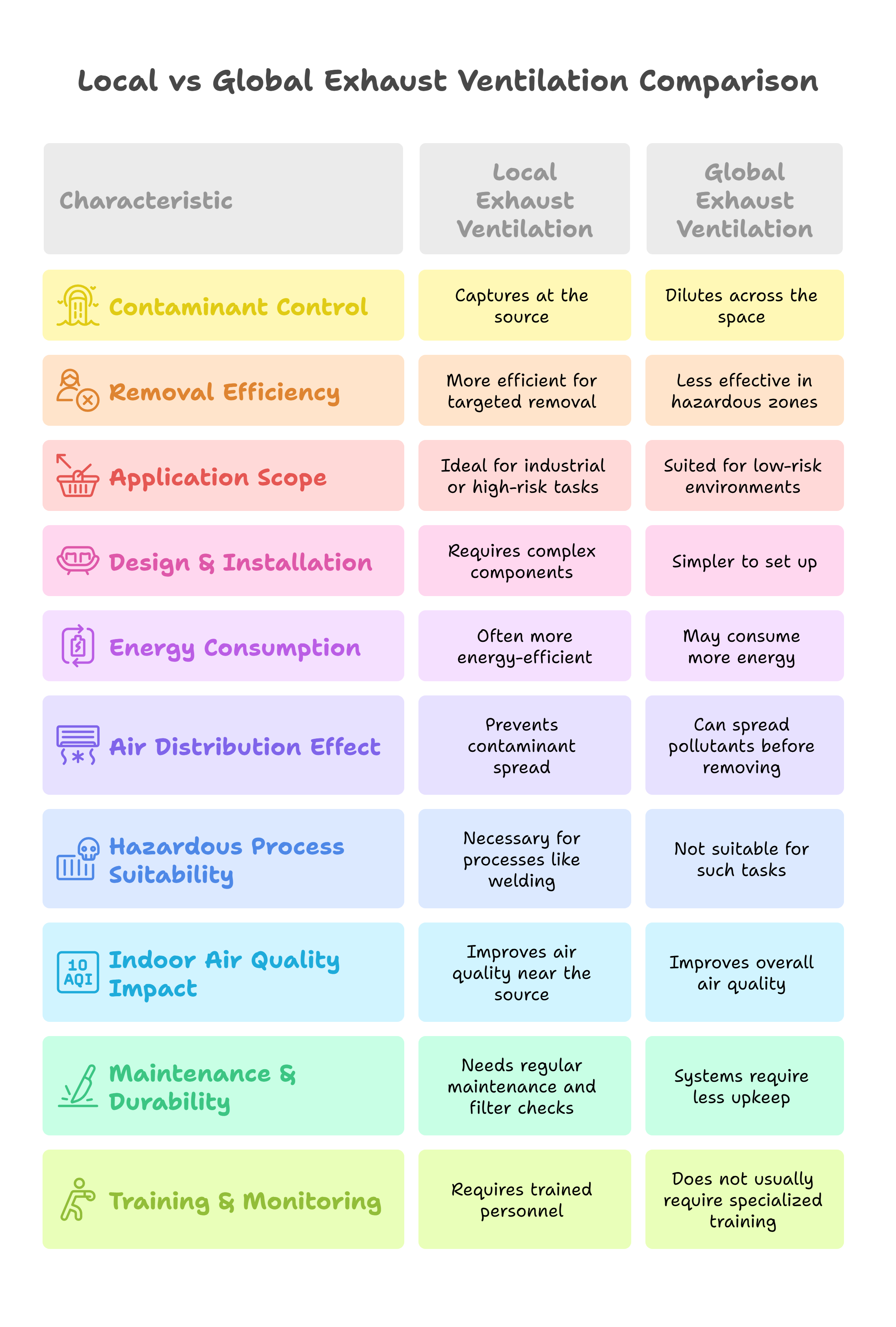
As you know, the biology lab is one of the most complicated school laboratories in terms of lab supplies. Today, we present you with the list of biology lab consumables. In this list, you will find the 20 most common bio lab consumables as per CBSE ICSE IGCSE IB State Board curriculums. You can use this list to formulate your own bio lab supplies requirements because these are the most common biology lab consumables useful in most biology practicals.
To be sure, the bio lab supplies can be divided into certain categories depending upon their type or usage. There are some basic lab glassware and support items that are disposable and/or one-time use only. There are various types of chemicals, which can be categorized into inorganic chemicals, various acids, and reagents.
Let’s proceed to the list of biology lab consumables below.
Support items and glassware
- Cover slips
- Slides
- Filter Papers
- Blades
- Pins
- Twine Thread
- Cleaning Agent
- Capillary Tubes
Basic Liquid Items
- DM Water
- Glycerine
- pH Indicators
Reagents
- Benedict’s Reagent
- Fehling’s Reagents (A and B)
Inorganic Compounds
- Sodium Bicarbonate
- Sodium Hydroxide
- Copper Sulphate
- Iodine Solution
- Acids
Organic Chems
- Staining Agents ‒ Methylene Blue, Safranin
- Carbohydrates ‒ Sucrose, Glucose, Maltose
The above are the most commonly used consumable items used in biology labs at classes 11-12. We will now get into the details of these items in the laboratory consumables list for your benefit. Each of these items has its own specific usage in particular biology lab practicals, experiments, and demonstrations.
Cover slip
A cover slip is a small piece of transparent glass or plastic, very thin, 18 to 25 mm in width. They can be square or round in shape. Cover slips are used in the case of observing tiny specimens under a microscope. The specimen is put on a slide and then it is covered by a cover glass (hence the name) so that nothing outside touches it.
Slides
When you need to watch a specimen under a microscope, what do you put it on? A slide, that’s what. They are generally 75 × 25 mm in size and are basically small thin glass or plastic plates. Glass slides are most commonly rectangular in shape, but in some cases, square slides are used as well. Some advanced microscope slides have a microscopic grid etched on a surface to work with distance measuring. Some others have a positive static charge so that specimens and cover slips can stick to the slides easily.
Filter Paper
A filter paper is used to separate solid particles from a fluid mixture. Generally, you take a piece of filter paper, fold it to make a kind of cone or bowl, and place it in a funnel and pour the liquid in it. Working like a sieve, the semi-permeable nature of the filter paper lets the liquid pass through but stops the solid granules. It is great to clean up a solution from impurities.
Blades
Stainless steel safety blades are a multipurpose cutting device used almost everywhere on earth. They are extremely sharp, and so you can use blades to cut fine shapes or lines in most soft materials. In a biology laboratory, you will be using blades to cut up very thin samples from various plants.
Pins
One of the most common general lab consumables, pins are used in a biology laboratory to hold various items in place, mostly on boards or dissecting trays. There are also some experiments that require pins to mark places ‒ for example, the potato osmometer experiment.
Twine Thread
Good thread is always good to have in your pocket. In a bio lab, you may expect to use thread to hang things from a stand or tie up large specimens. In paper chromatography, you will need to hang the filter paper by a thread.
Cleaning/Disinfecting Agent
As a bio lab works with a lot of stuff that can be considered ‘dirty’ (like microbes, biomass, chemicals, etc.), it needs to clean things up a lot. For this task, lab technicians employ many kinds of cleaning materials ranging from pure alcohol to soda. A safe and healthy biology lab will consume cleaning and disinfecting agents on a daily basis, so this will be a common expense to a lab manager.
Capillary Tube
A capillary tube is an extremely thin glass or plastic tube. It has such a small inner cavity diameter that barely a hair can pass through ‒ 0.5 to 2 mm. These tubes are used in experiments that deal with the capillary actions of a fluid. You can also use them to collect fluid samples. Since they are impossible to clean normally, they are a use-and-throw item.
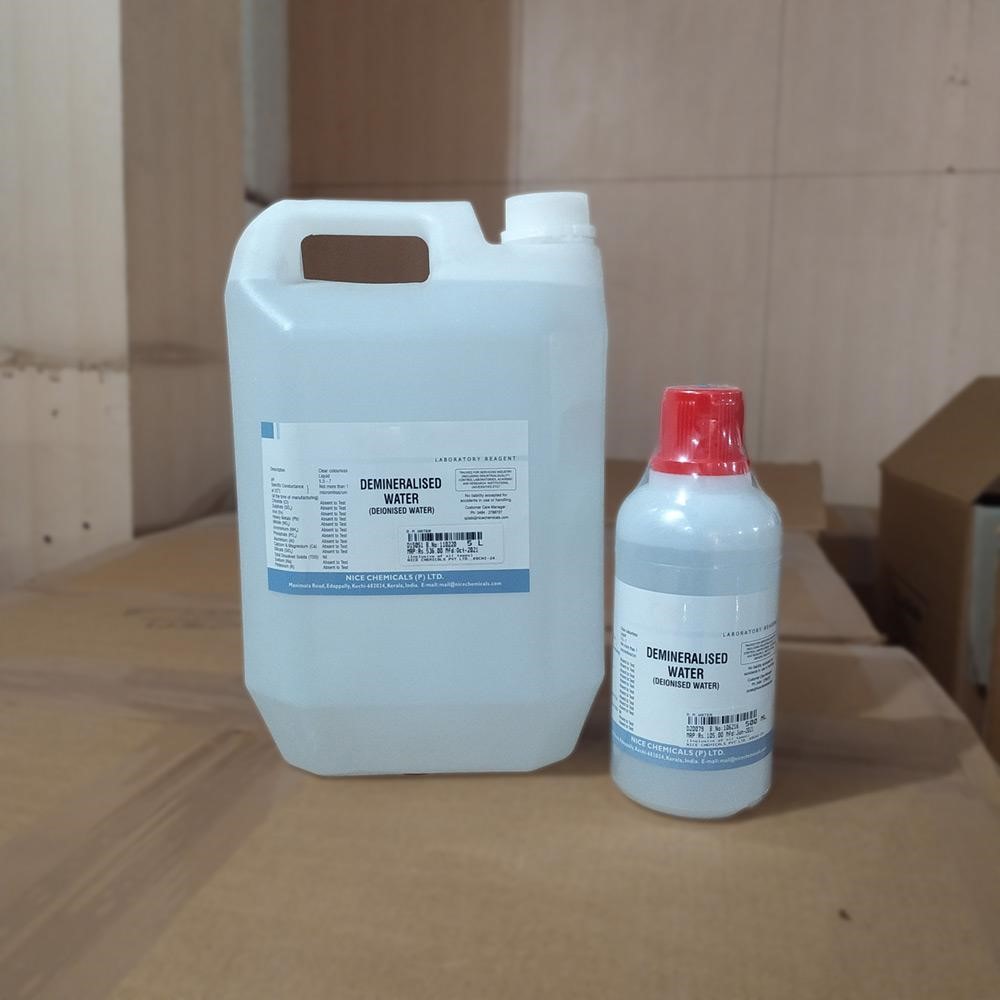

DM Water
Demineralized (DM) or deionized water is among the cleanest and purest forms of water you can buy on the market. It has almost no ions to speak of, so it is the best universal solvent in the world and would provide the cleanest solutions of water-soluble chemicals. Since it is also free of bacteria and other microbes, this water is used in bioscience labs almost exclusively. You can buy 95% pure DM water jars from Labkafe.
Glycerine
A pretty dense and viscous fluid, bio labs use glycerin mostly in preparing slides to display under a microscope. Technically though, it is known and available in lab consumable shops as glycerol. You may already be very familiar with this since it is a prime ingredient of cheap hand sanitizers. Also, you may have used glycerine soap at home.
pH Indicators
Indicator papers like Litmus papers, and their solutions, are very very common in chemistry and biology labs. They are used in figuring out how acidic or alkaline a solution is. These days, we don’t use Litmus papers or solutions as much ‒ instead, we use the universal indicator. It displays much smoother and more responsive color changes than plain old Litmus.
Benedict’s Reagent
One of the most common reagents in most bioscience labs in any level of learning or research is the Benedict’s reagent . It shows clearly the presence of reducing sugars in a given solution. Generally a nice toothpaste blue in color, it turns amber when it encounters glucose, fructose, maltose, etc.
Fehling’s Reagents
There are two Fehling’s Reagents (A and B), of which the first is basically a copper sulphate solution (nice color, huh?) and the second is a strongly alkaline solution of Rochelle salt . When in use, you can combine them to produce a lot of copper ions which react quickly with any reducing sugars present in the vicinity. As a result, some reddish copper oxide will appear at the bottom of the solution in question. They are also called Fehling’s Solutions .
Sodium Bicarbonate
We all know this as baking soda, but sodium bicarbonate is a highly consumable substance in the biology labs too. Since it is an acidic salt, you can use this to increase the acidity of a buffer solution. Practicals that need this are food tests and photosynthesis experiments ‒ extensively.
Sodium Hydroxide
Known best as caustic soda and the most common cleaning ingredient, sodium hydroxide is best at producing buffer solutions or solutions of specific pH values. Food tests would need this, as well as some other experiments. It is one of the cheapest lab supplies available from lab consumable suppliers.
Copper Sulphate
Perhaps one of the most recognizable salts in biology and chemistry labs, copper sulphate solutions of various concentrations are highly useful in biology lab practicals. Most notably, you will need to use 1% CuSO4 solution in the biuret tests. It is also a good fungicide, so you may have seen copper sulphate solution in preserving raw vegetables. Interestingly, this is also one of the prime ingredients of Benedict’s and Fehling’s reagents.

Iodine Solution
The main ingredient in the starch identification experiment, the Iodine solution is very useful in biology labs. It is a simple but very effective indicating agent that will be used almost every day in a higher secondary biology lab.
Acids
What is a laboratory without acids? Three inorganic and one organic acid are very useful in all kinds of bioscience labs. Hydrochloric acid is good for making buffer or pH-savvy solutions. When you need to create oxygen-nitrogen compounds in certain experiments, use nitric acid . Sulphuric acid is most needed in the Pettenkofer test of bile salts. Acetic acid is a very common organic acid used in various lab experiments too.
Staining Agents
When you need to view a microscopic sample, you have to ‒ almost always ‒ use some sort of artificial color to stain the sample in order to view it comfortably. There are many such staining agents available for different scenarios ‒ but methylene blue and safranin are the most common dyes seen in HS level bio labs.
Carbohydrates
A biology lab would need a lot of organic compounds naturally found in living organisms ‒ and carbohydrates are the most common of them. Sucrose , glucose , and maltose are the most common carbs and a bio lab will consume them in volumes. Getting fat is optional!
All of the items above are easily available from any good lab supplies vendor like Labkafe. These lab consumables are already available as part of the biology lab packages for classes XI/XII. The chemicals and reagents we provide are of the best quality available in India, and would give you good results in your lab experiments. We have customized packages for all educational boards in India like CBSE ICSE ISC IGCSE IB and State Boards. Contact today to get prices!








Leave a Reply