Chemistry is the branch of science concerned with the substances of which matter is composed, the investigation of their properties and reactions, and the use of such reactions to form new substances. And a laboratory gives us a perfect chance to build upon the basics taught in class.
Purpose of chemistry laboratory
- Ability to solve chemical equations using laid out procedures based on well-established scientific principles.
- Students are expected to be able to use chemical theories to explain and predict observable phenomena.
- Competence with lab equipment and measuring devices are expected in addendum to precise recording of data.
Essential furniture
A typical chemistry laboratory has workbenches with sink, water faucet and reagent rack. These workbenches can also have base cabinets to store glassware, apparatus etc. Special cabinets are used to store chemicals. Workbenches are fitted with necessary water and gas connections to conduct various experiments. Apart from these, Teacher’s table, first aid kit, safety chart, and fire extinguisher are other necessary requirements.
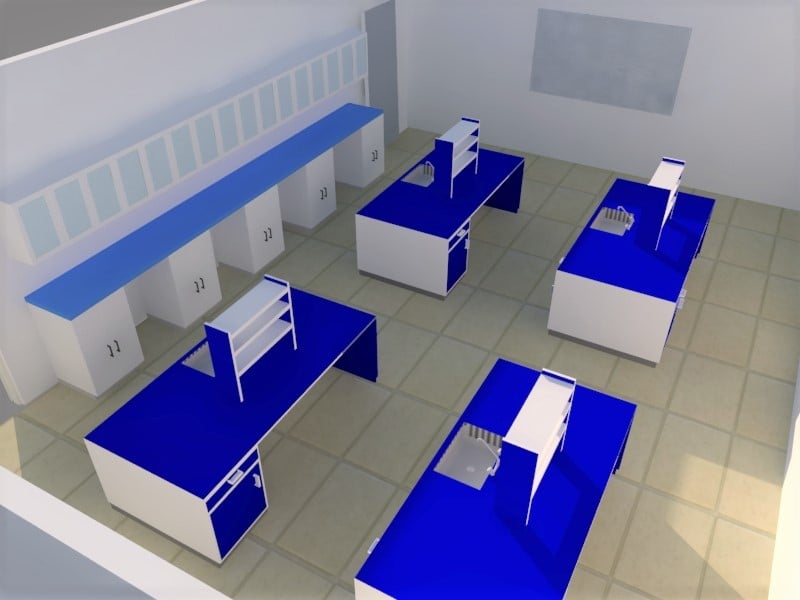

A detailed description of each of these components is given below.
WORKBENCH
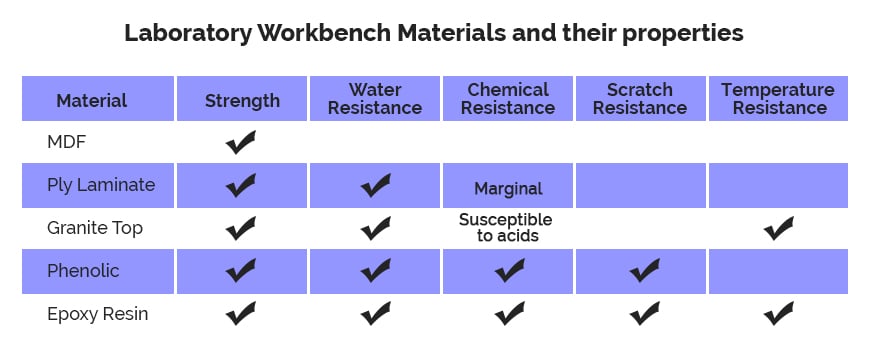
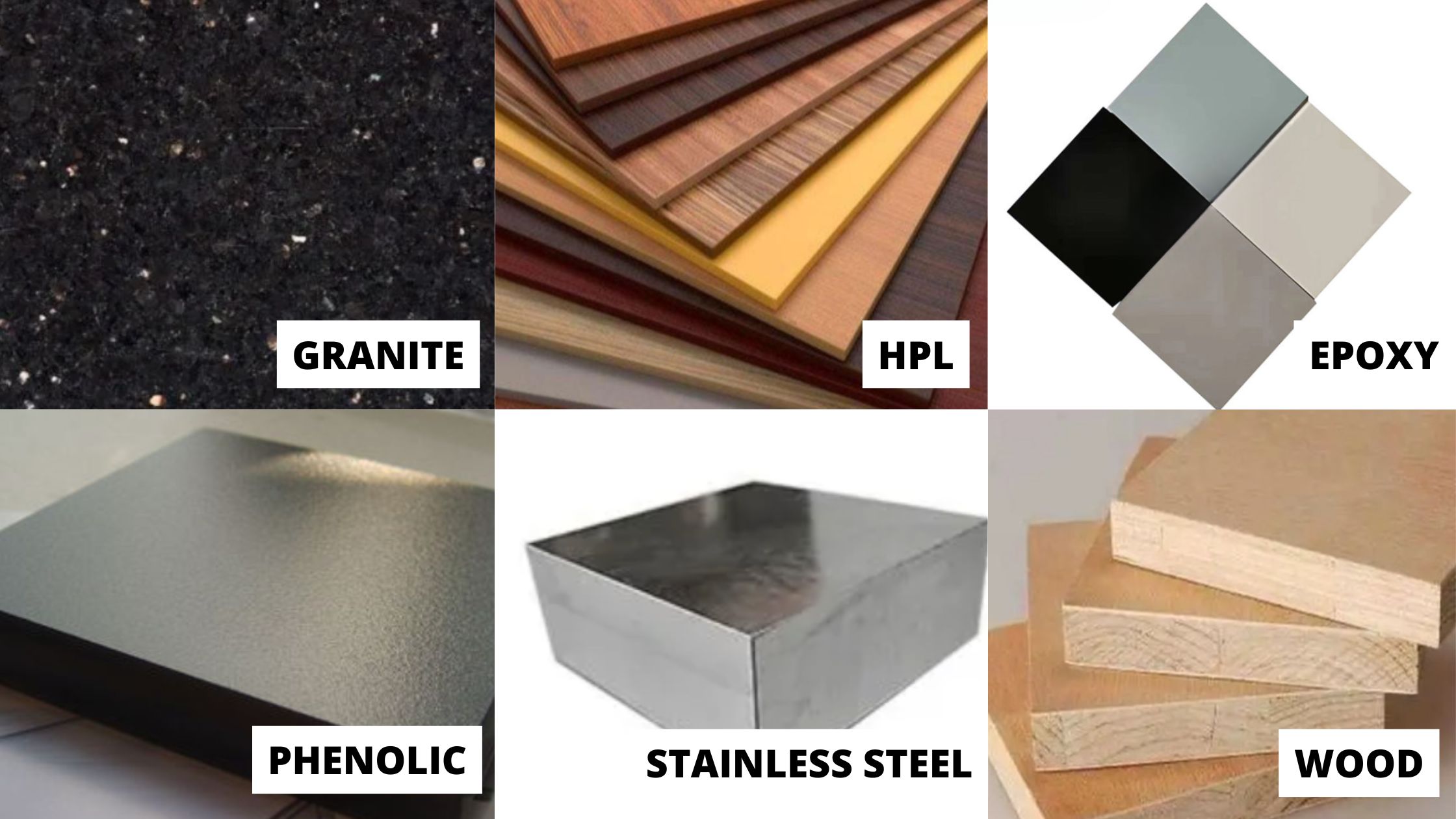
A workbench is the backbone of a laboratory. Especially for a chemistry laboratory where one is dealing with corrosive chemicals, high temperature, wet conditions, glassware etc. to name a few, the quality of table top material is crucial to withstand above-mentioned conditions and at the same time, it ought to be durable enough. Following materials are generally preferred:
- MDF: Medium-density fibre board (MDF) is an engineered wood product made by breaking down wood residuals into wood fibres, combining it with wax or resin binder to form panels by applying high temperature and pressure. It is denser and stronger than particleboard but has poor water resistance.
- Ply Laminate board: It has a multi-layered structure with the top most material providing chemical resistance while base layers providing strength. It provides better resistance than MDF even though porosity is of higher grade. Another common practice is of adding a layer of aluminium sheet over it in order to curb it.
- Granite Top: Granite is an igneous rock composed of silicates such as feldspar or quartz. Although it provides significant resistance to water but is vulnerable to acids. A common occurrence called etching is basically dulling of granite top surface due to reaction with acids.
- Phenolic board: Phenolic board is made by bonding plywood with waterproof phenol resin adhesive overlaid on both sides with the phenol film. Overlaying surface is smooth, glossy and hard making it withstand abrasion, moisture-resistant (especially boiling water), and chemical resistant (commonly used chemicals, dilute acids, and alkalis).
- Epoxy Resin board: Epoxy Resin board is made by applying a coat of epoxy resin over desired board. Epoxies generally out-perform most other resin types in terms of mechanical properties and resistance to environmental degradation. It forms a layer over base material preventing moisture and corrosive chemicals from seeping in. Also increasing its temperature and scratch resistance.
Available space in a lab plays a crucial role in the overall working of the lab as well as in its safety compliance. A detailed account has already been discussed in 9 Things to Consider Before Designing Your Laboratory. Also, the capacity of a lab for students conducting experiments simultaneously is equally important bullet that can’t be neglected for better workflow. To optimize the given space, workbenches are designed in two varieties as below:
- Island Workbench: As the name suggests, island workbench can be accessed from all the sides. Normally an Island workbench of Standard size (8’X4’) can accommodate 6-8 students at a time and it can vary as per the need.
- Wall Facing Workbench: They are used in tandem with Island workbenches. They can accommodate 3-4 students in every running 8’ & this is totally carved out as per the requirement of individual rooms. It totally depends upon Wall-to-Wall distance & also gets affected by the pillar hindrances in between.
The common size for a workbench is 8’ by 4’. It is so because ply normally comes in a standard size of the aforementioned. Hence to optimize the cost this is a common practice by us.
If I bought 4 Mangoes for Rs 40, the price for a dozen would be: 120 INR(We used Unitary Method to solve the problem)But on the contrary if you purchase a Workbench (8’X4’ which is a standard size of the raw material & there won’t be any cutting loss), any other size of workbench would bear more cost than the normal Unitary Method Formula. Hence it is advisable to not go for unusual sizes until & unless one wishes to go for lavish designs.
REAGENT RACK
A reagent rack holds ready-to-use reagents and glassware to be used during experiments. It clears the workable area during the experiment and prevents accidental spillage or breakage. It is usually mounted on top of workbench.
It comes in various designs namely single and double-tiered.
SINK
Sinks are necessary for waste disposal. They come in various options like Stainless Steel, Poly propylene (PP) etc. Most of them are inert to all kind of acids, alkalis, and solvents. PP sinks are preferred as it minimizes glassware breakage on impact.

FAUCET/TAP
Taps are required for glassware washings especially like burettes and pipettes as well as for experiments.
BASE CABINET
Base cabinets are storage cabinets beneath the work top. They are used to store major lab equipment and consumables locally. Pre-storage practices should be adopted and stocking of necessary materials be done at the start of each class for the accountability of inventory stock & regular monitoring of breakage in any case.
They are made of vivid materials as such CRC Sheets, MDF, Particle Board & Ply-Laminate. Many institutions go for Base Cabinets as separate entities; some go with the attached Base Cabinet to Work Tops.
CHEMICAL STORAGE UNIT/WALL CUPBOARD
Chemical Storage Unit is a wall cupboard used for safely storing small amounts of chemicals or hazardous materials. It can also be used to store glassware, equipment etc.
FUME HOOD
A fume hood is a type of local ventilation device that is designed to limit exposure to hazardous or toxic fumes or vapors in the lab.
LAB STOOL
Lab Stools are easy to handle and don’t cover a lot of space. It comes with adjustable height and offers a comfortable resting place during the course of experiments.
Essential Equipment/Glassware
Following are must-have equipment/glassware in a chemistry laboratory.
BEAKER
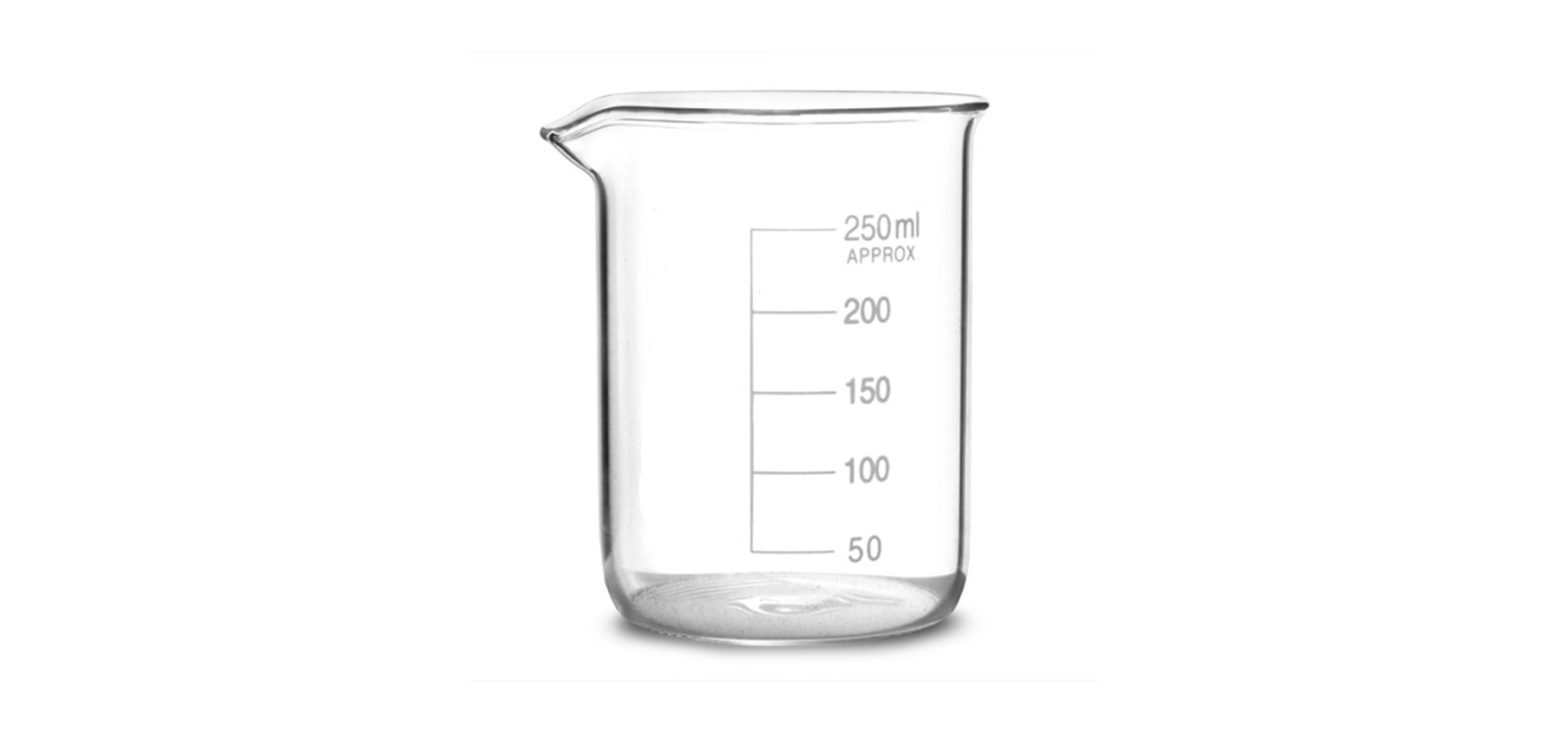

A beaker is used for mixing, stirring and heating chemicals. It comes in a range of sizes. Majority of beakers come with spouts on the rim to help with easy pouring. Also, some of them come with marking to measure the quantity of liquid in them but this practice is not too reliable. A watch glass is generally used to cover the opening to prevent it from contamination.
ERLENMEYER FLASK/CONICAL FLASK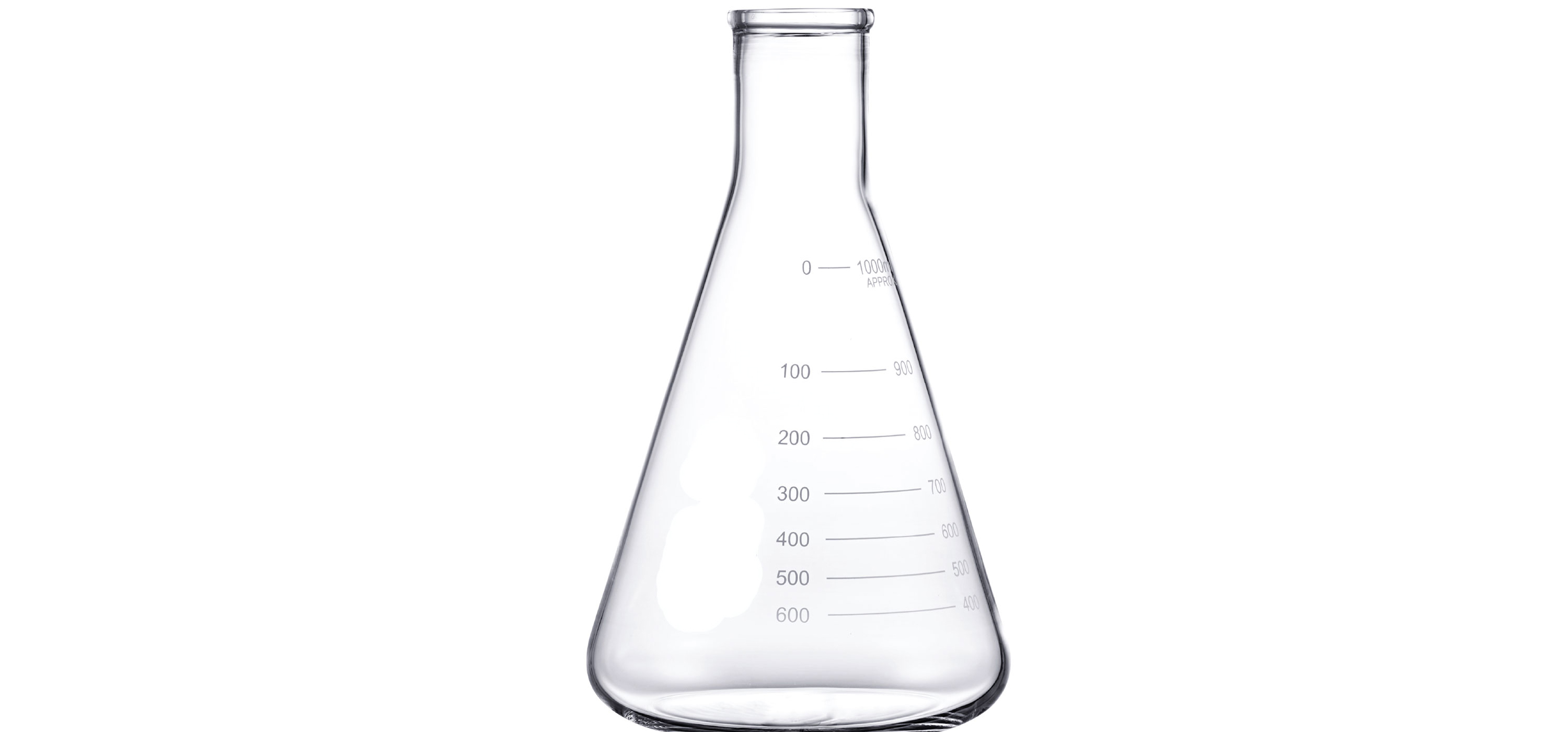
Conical flask gets its name from its shape an inverted cone with a narrow neck extending from the conical base. This shape allows easy mixing without the risk of spillage. The narrow neck’s opening allows for a rubber/glass stopper further negating spillage during mechanical shaking and prevents contamination. Also it can easily be clamped to a ring stand prior to heating. It comes in a range of sizes for different capacity. It too comes with marking on the neck but should only be considered for estimation.
BOILING FLASK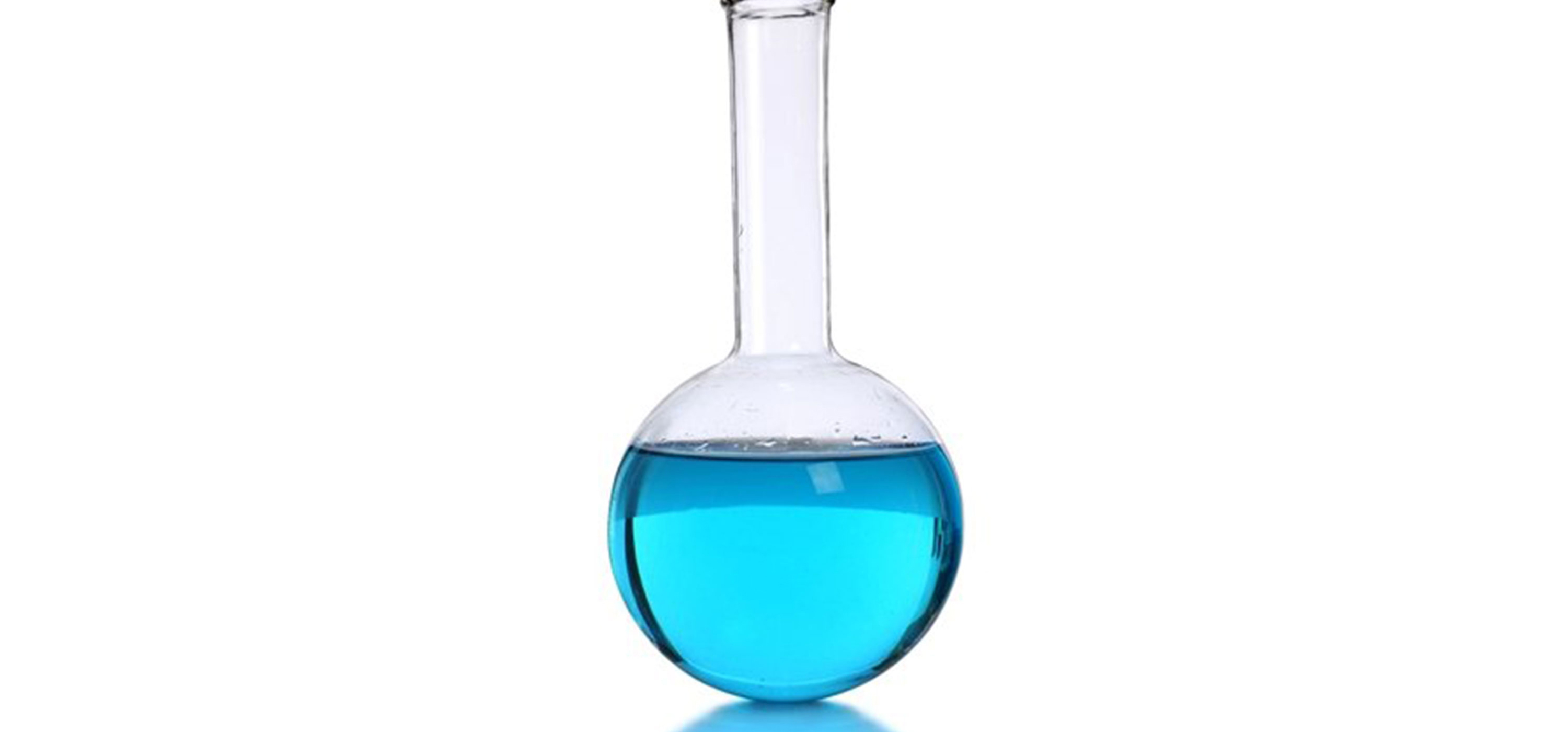
Boiling flask, also known as a Florence flask, it has a round bottom and a long neck extending from the base. It too comes in the range of sizes with It is used to hold liquids and can be easily swirled and heated. It can also easily be capped by rubber or glass stoppers. Once again, safety dictates that this flask never is heated when capped. Pressure build-up and explosions can and do occur.
TEST TUBE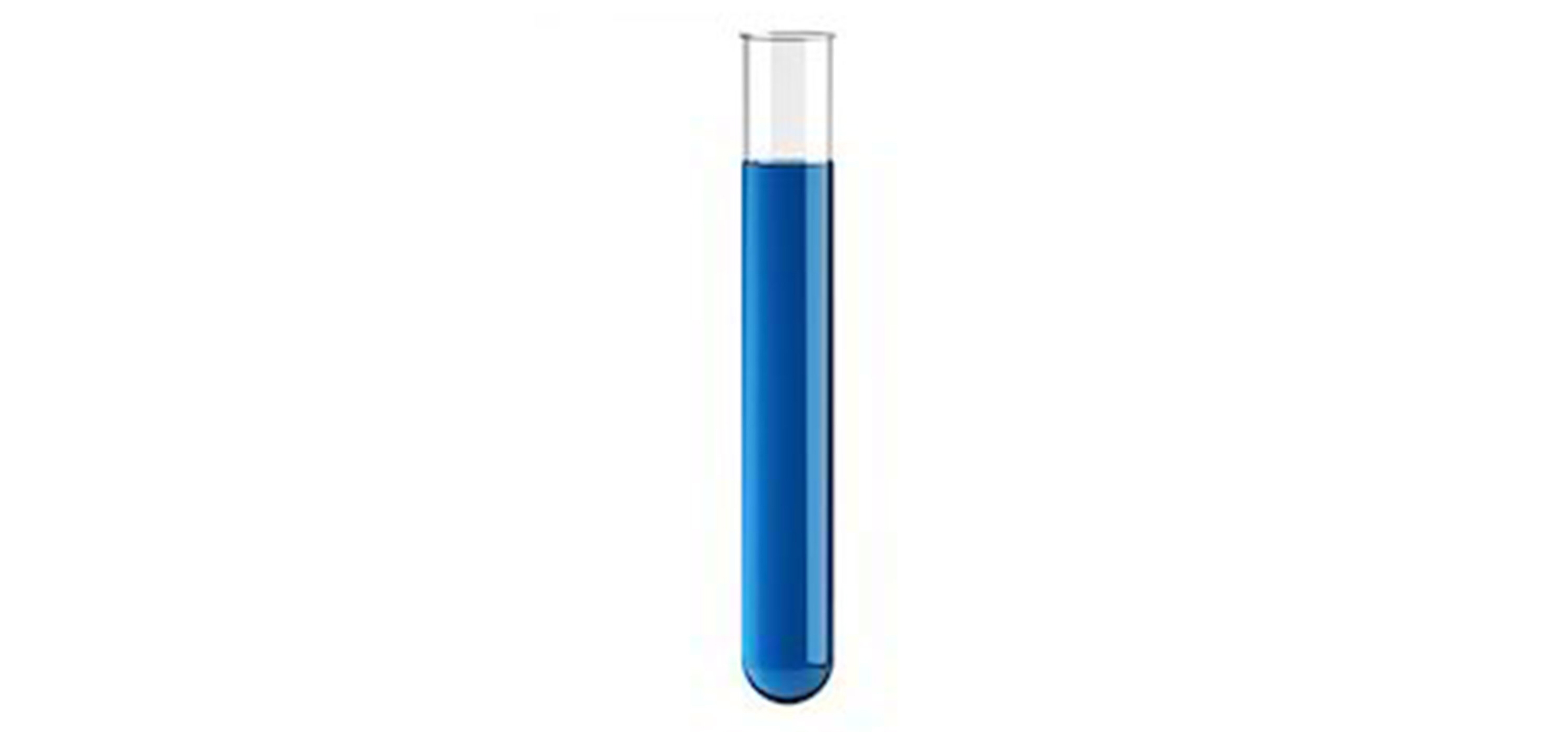
A test tube is a glass tube with an open end and a round closed end. It holds small quantities and is used for qualitative assessment and comparison. The open end can be easily capped with a rubber or glass stopper. They are also easily capped with a rubber or glass stopper.
WATCH GLASS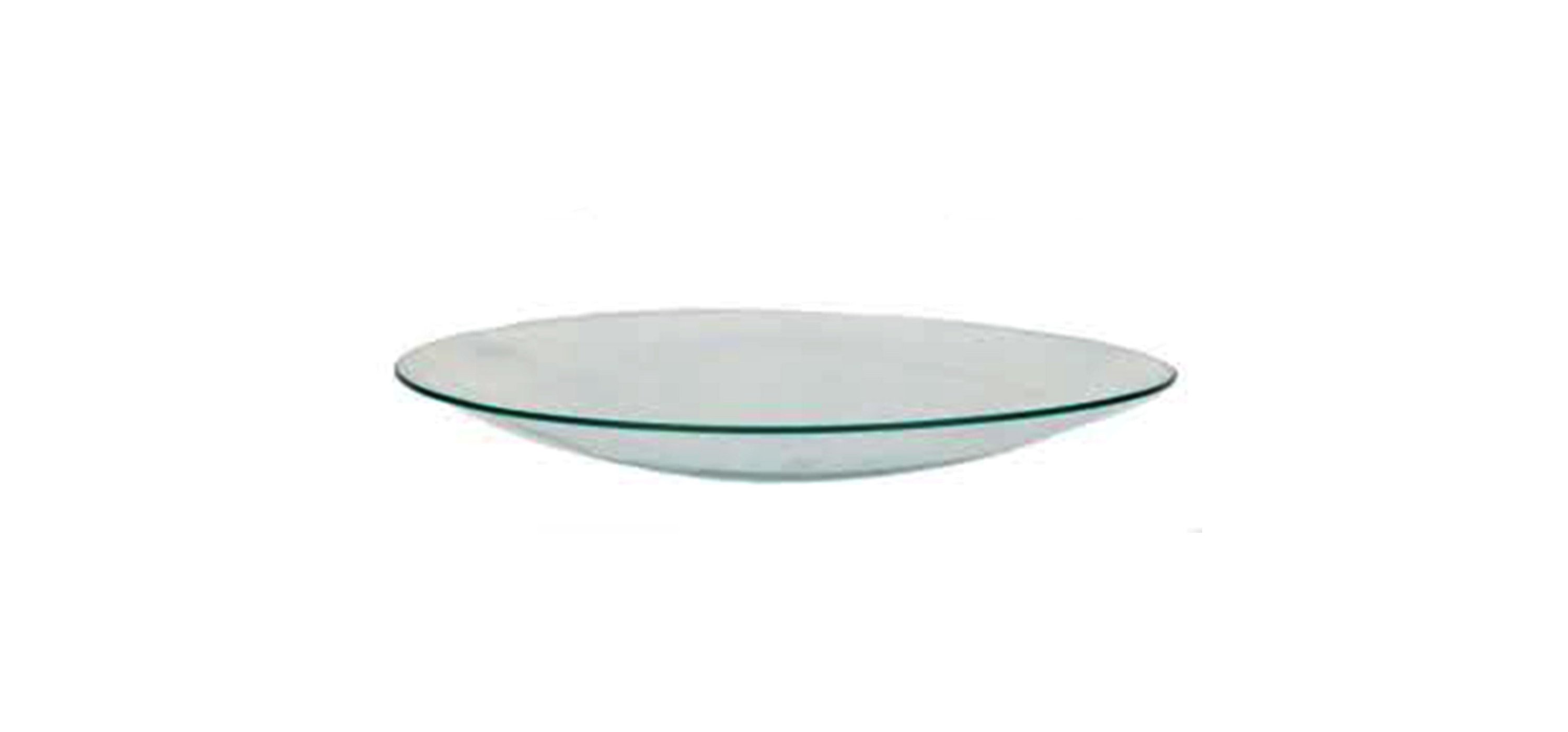
A watch glass is a round concave piece of glass. It can hold a small amount of liquid or solid. It used for evaporating liquid and also can function as a cover for a beaker.
CRUCIBLES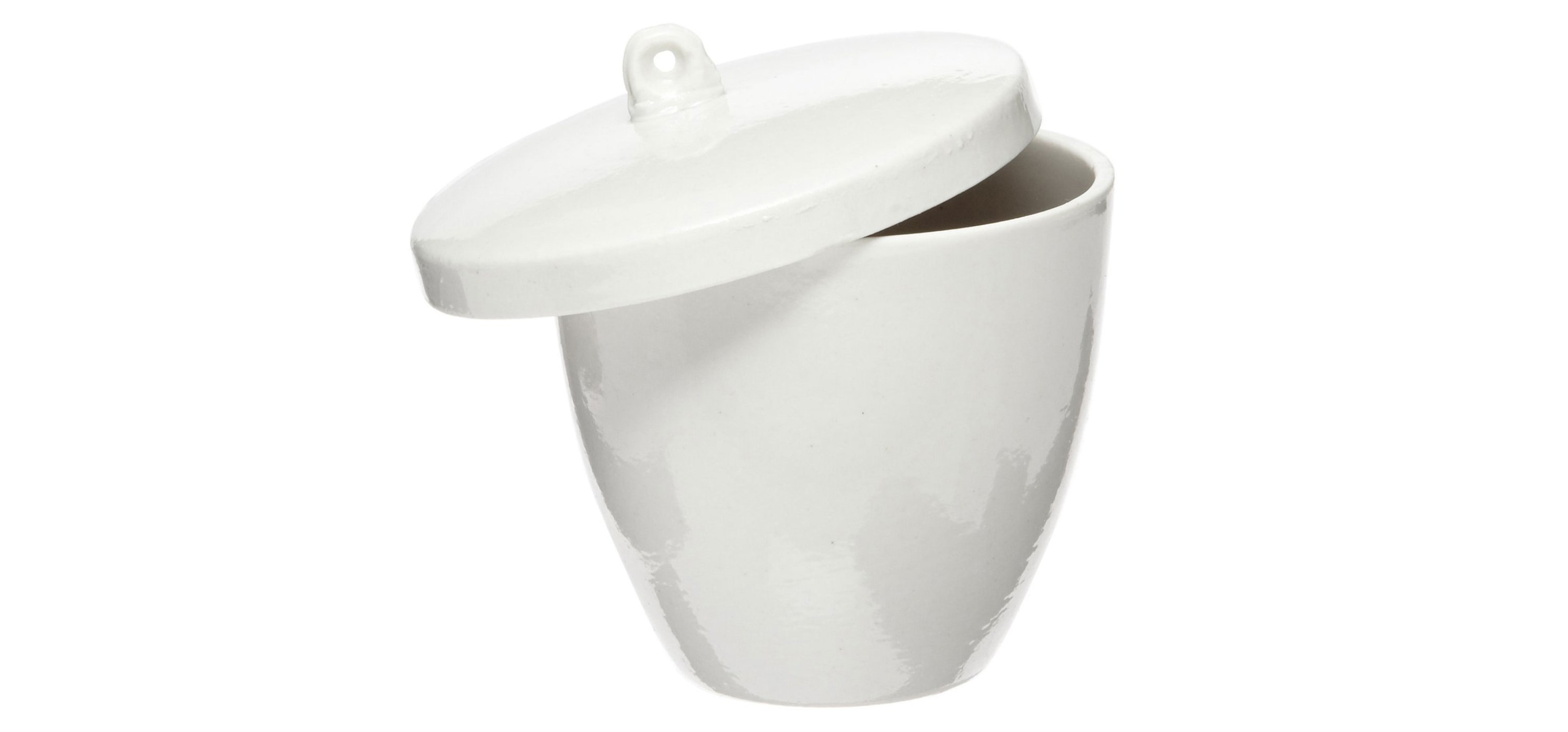
A crucible is a small cup that can withstand extreme temperatures. They are used for heating substances and come with a lid. It can be made from any material that can withstand high temperature.
FUNNEL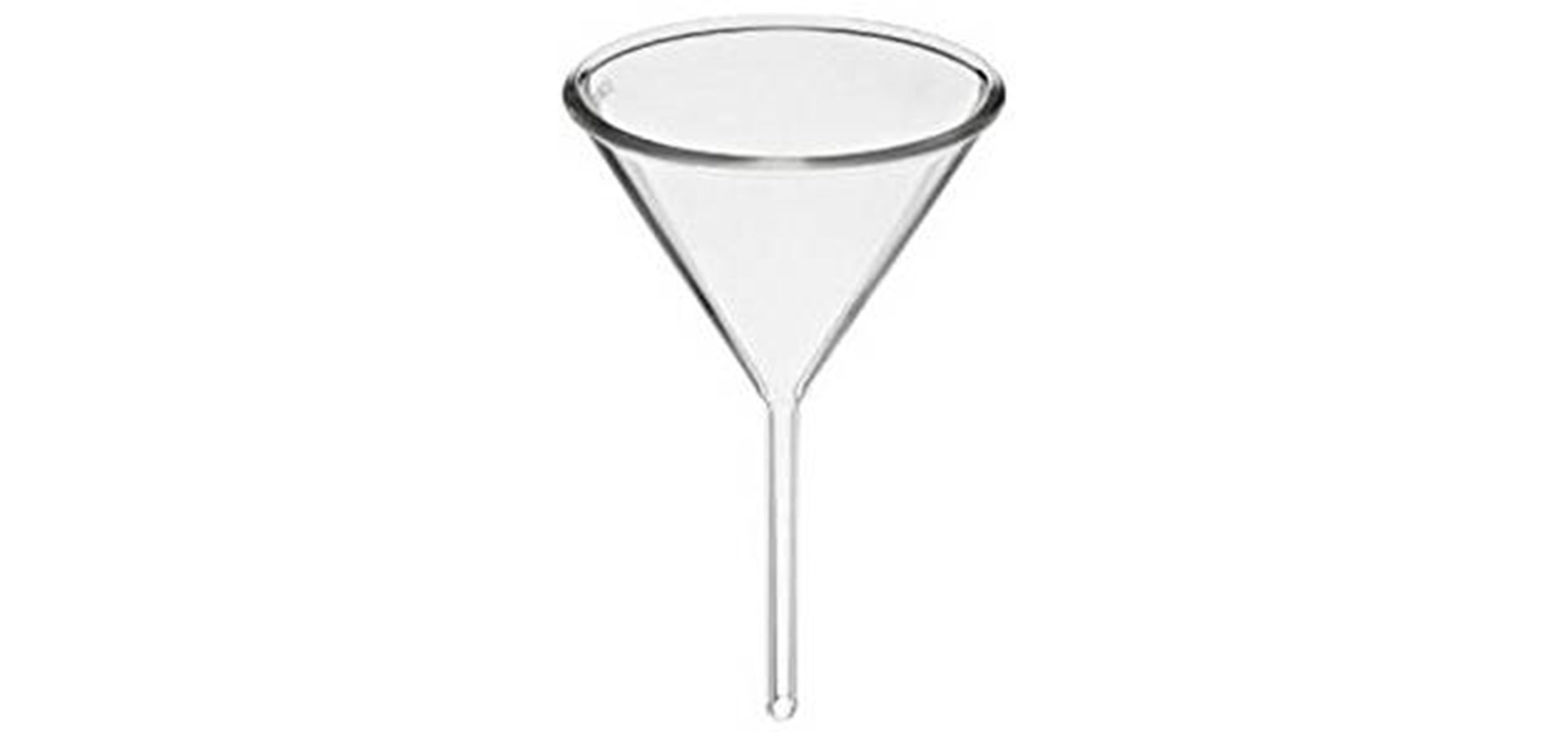 
A funnel is used to transfer liquid or fine-grained solids into small mouth containers. Its conical mouth and cylindrical bottom prevent spillage. It is usually made of glass or plastic.
GRADUATED CYLINDER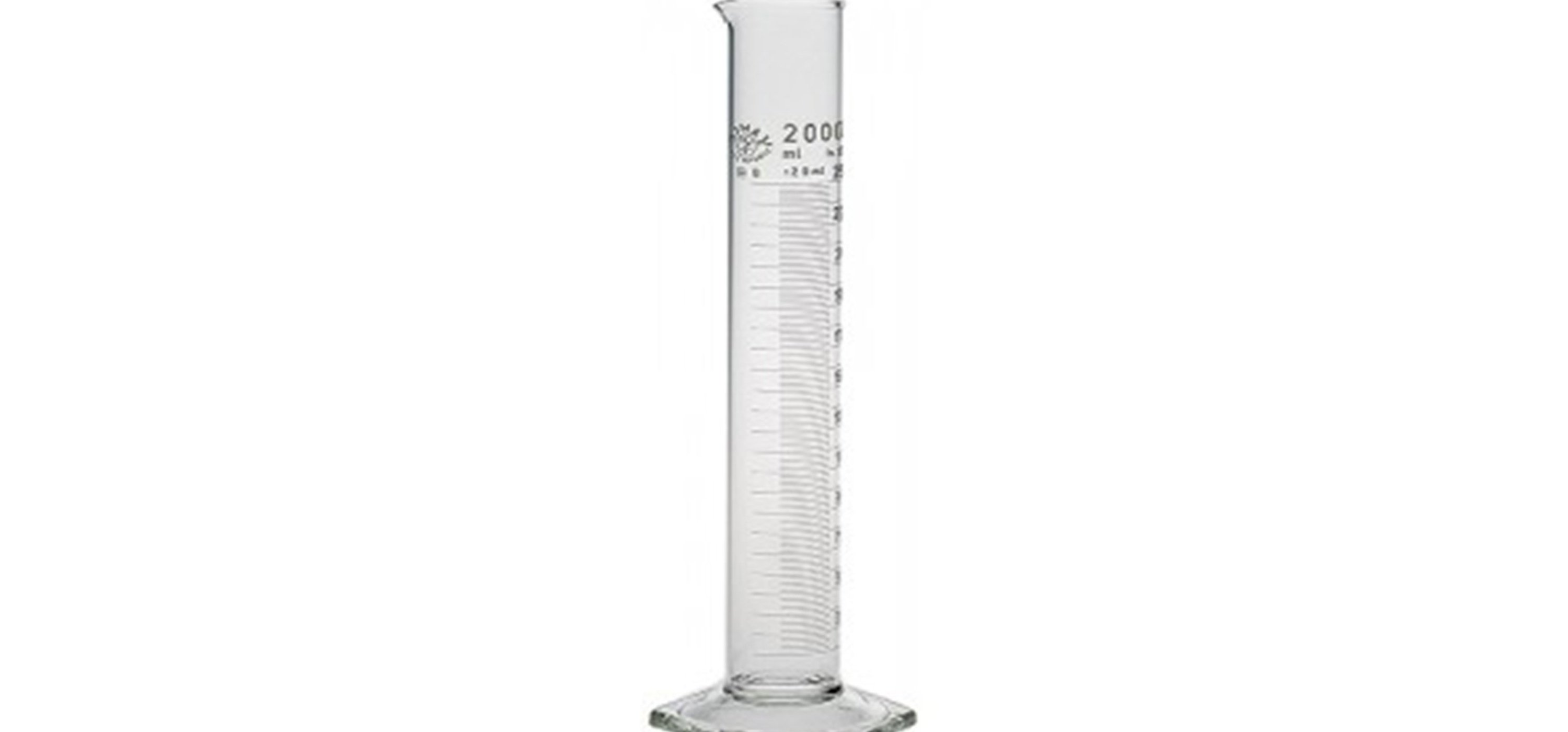
A graduated cylinder, measuring cylinder or mixing cylinder is used to measure the volume of a liquid. It has a narrow cylindrical shape. Each marked line on the graduated cylinder represents the amount of liquid that has been poured into the cylinder. The liquid around the edges will be higher than the liquid in the center, sloping down like the sides of a trampoline when someone is standing in the middle. This is called the meniscus. Line the lowest point of the meniscus up with the nearest marking, keeping the cylinder level to properly read the volume.
VOLUMETRIC FLASK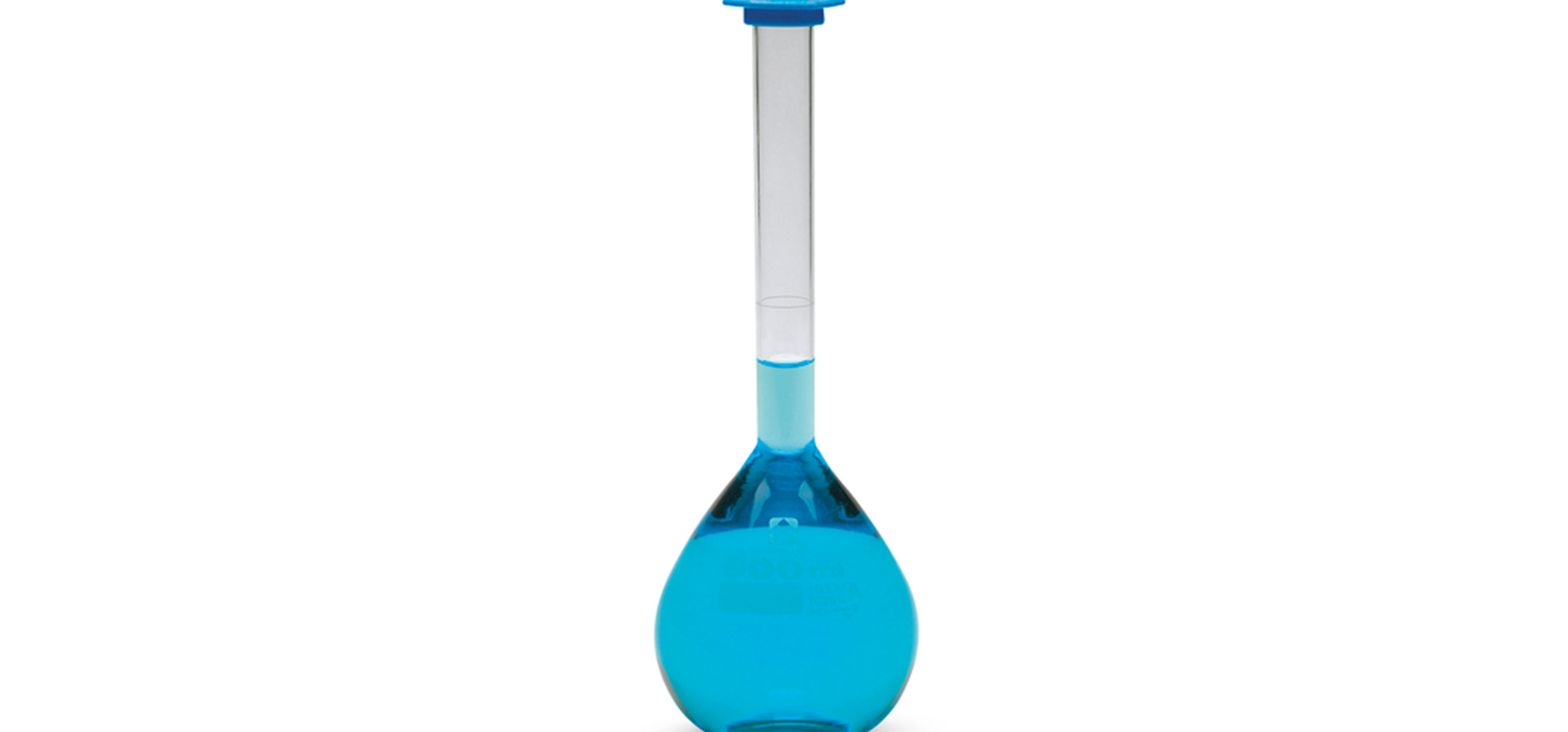
A volumetric flask (measuring flask or graduated flask) is a round flask with a long neck and flat bottom, calibrated to contain a precise volume at a particular temperature. Volumetric flasks are used for precise dilutions and preparation of standard solutions. They come with special caps that will not let anything in or out.
DROPPER
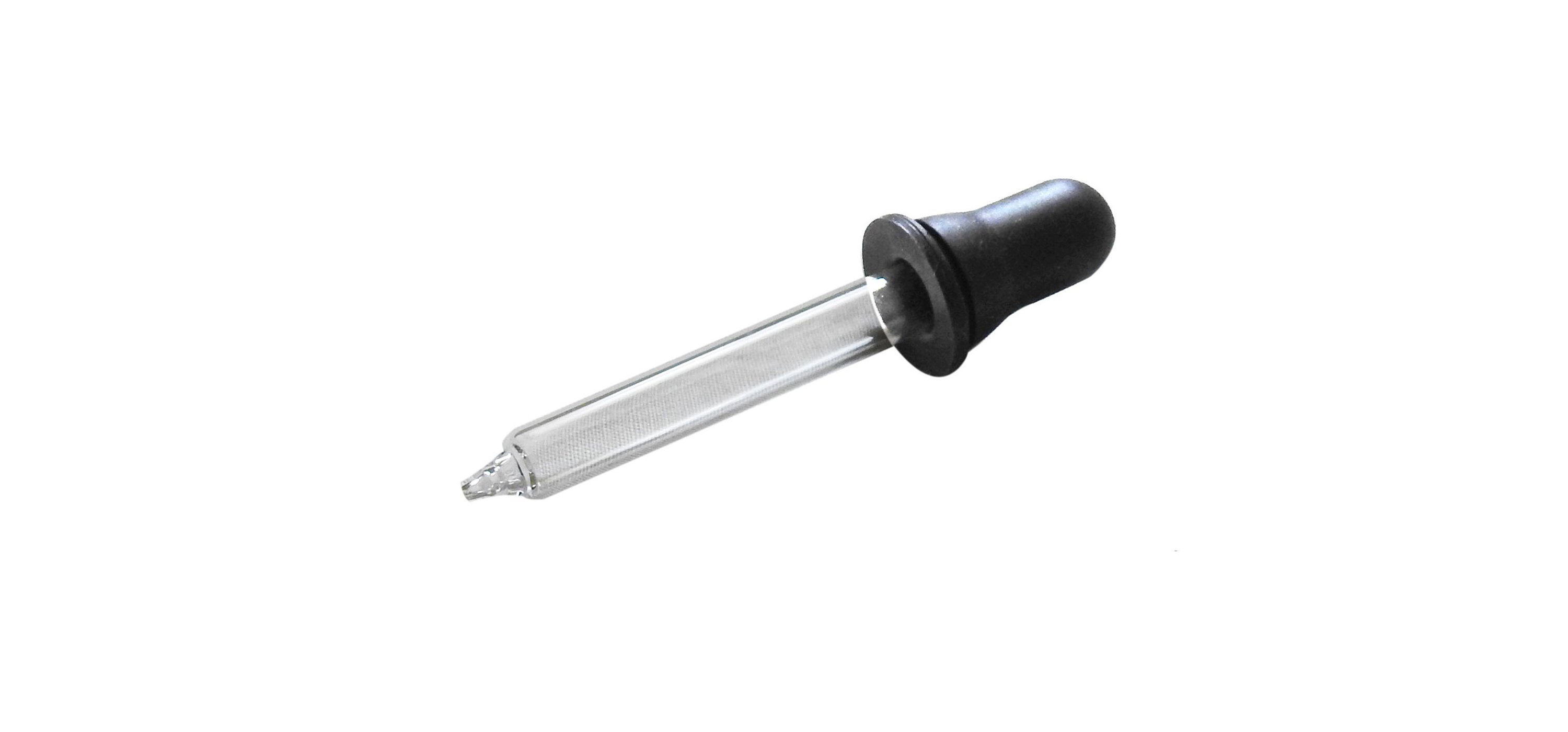

The dropper is a small glass tube with a narrow tip on one end and a rubber bulb on the other. They can hold a small amount of liquid by sucking it up which can then be squeezed out in small drops. These can be used to add an indicator to a solution about to be titrated.
PIPETTE
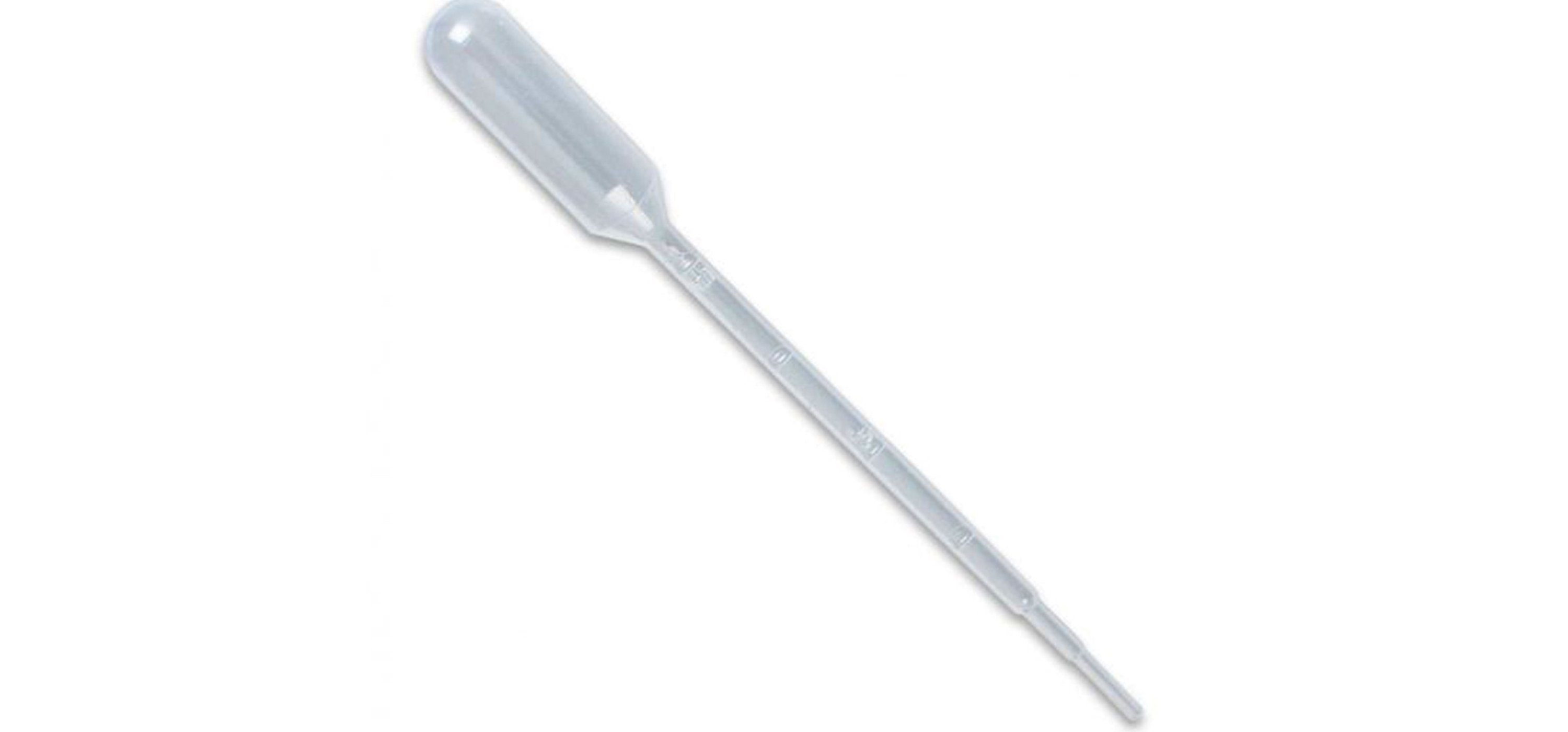

A pipette is used to transport a measured volume of liquid, often as a media dispenser. It comes in several designs for various purposes with differing levels of accuracy and precision. It generally works by creating a partial vacuum above the liquid-holding chamber and selectively releasing this vacuum to draw up and dispense liquid into another container.
BURETTE
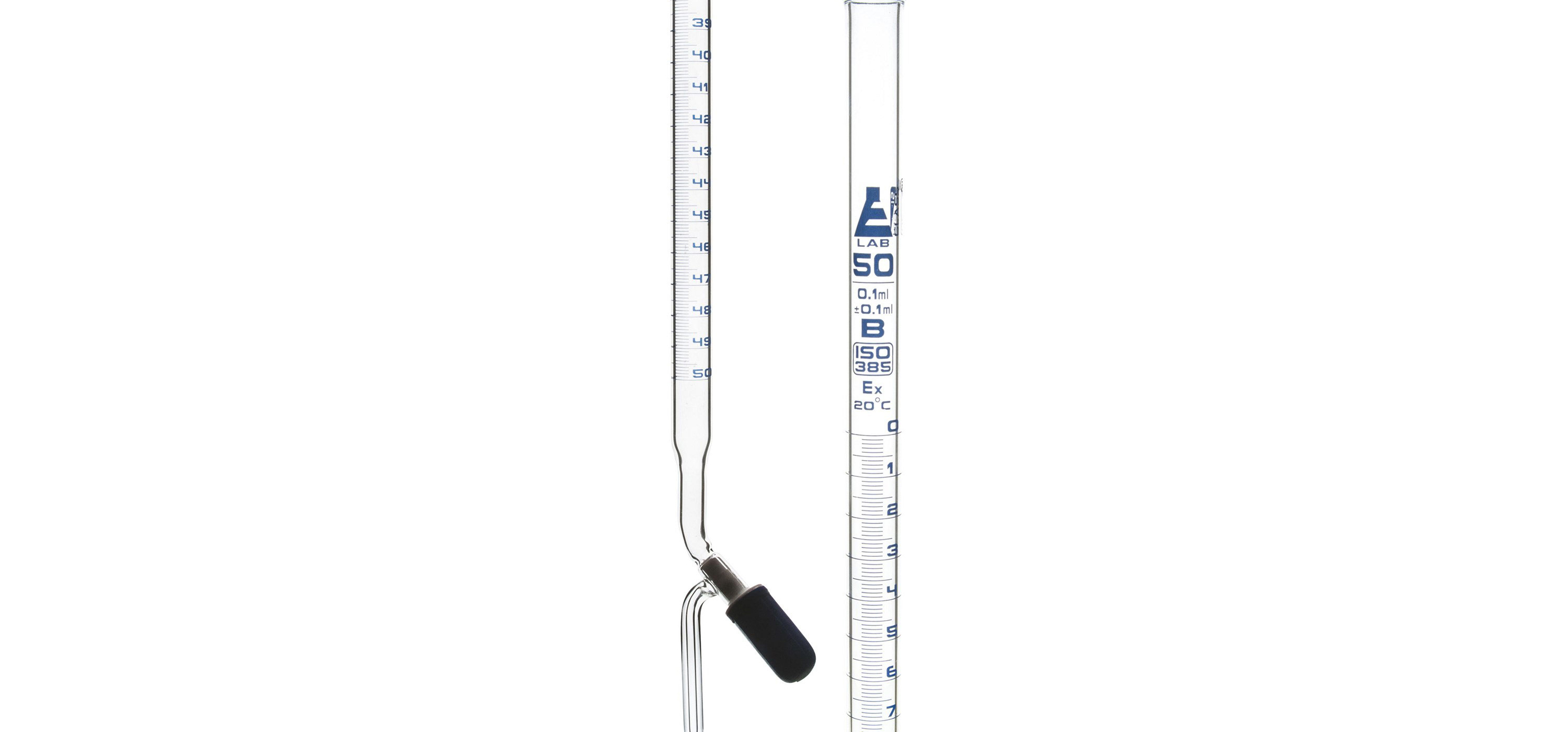

A burette is a long, graduated glass tube, with a stopcock at its lower end and a tapered capillary tube at the stopcock’s outlet. It is used for the dispensing of variable amount of a chemical solution and measuring that amount at the same time through markings along the length of the tube. The flow of liquid from the tube to the burette tip is controlled by the stopcock valve.
RING STAND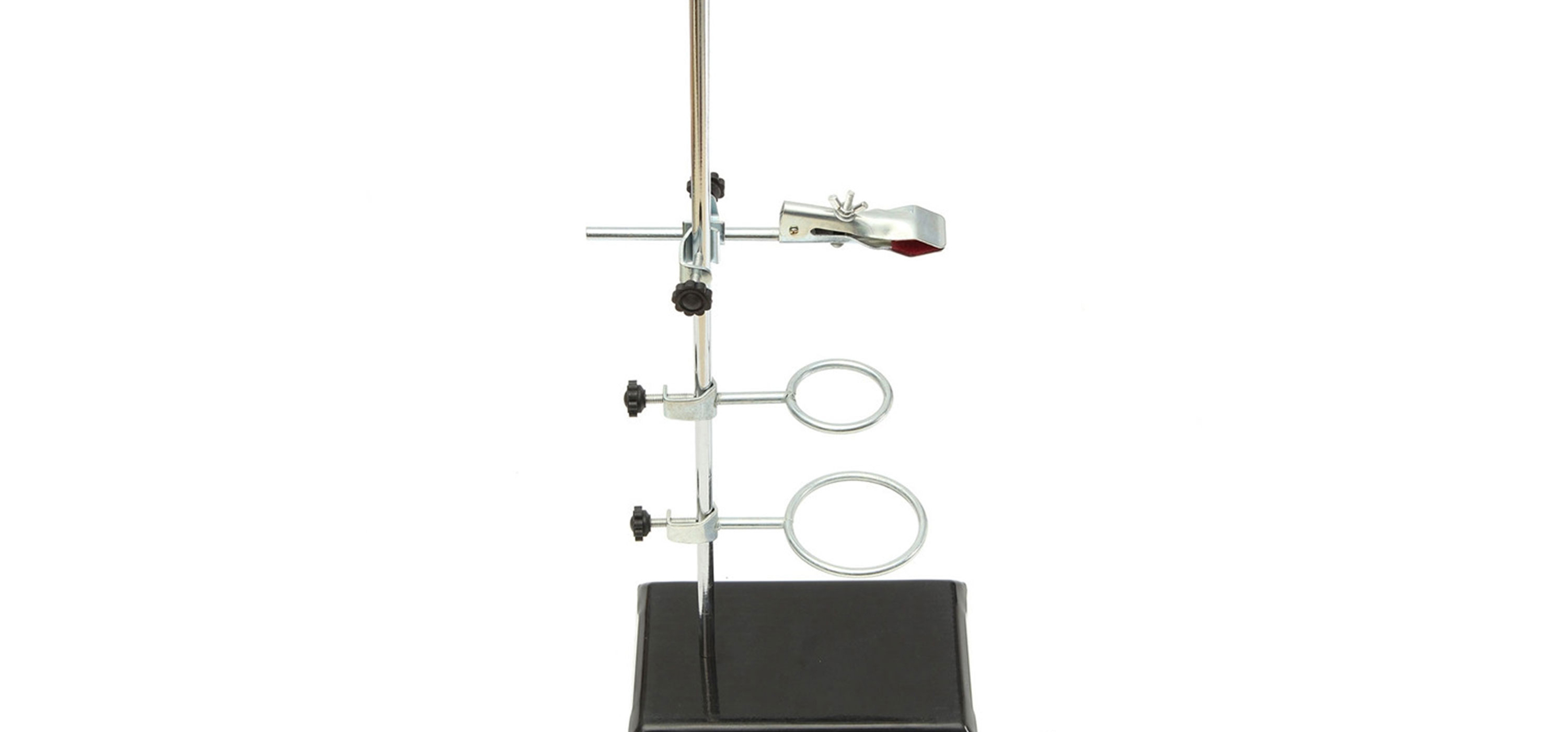
The ring stand is used to suspend burets, beakers, flasks, crucibles, etc. above other containers or, a Bunsen burner. When using a ring on the stand, there are usually other pieces necessary to accomplish the goal. Wire mesh is laid across the ring to distribute even heat and support the beaker. A clay triangle with an open center is used to suspend crucibles.
TONGS AND FORCEPS
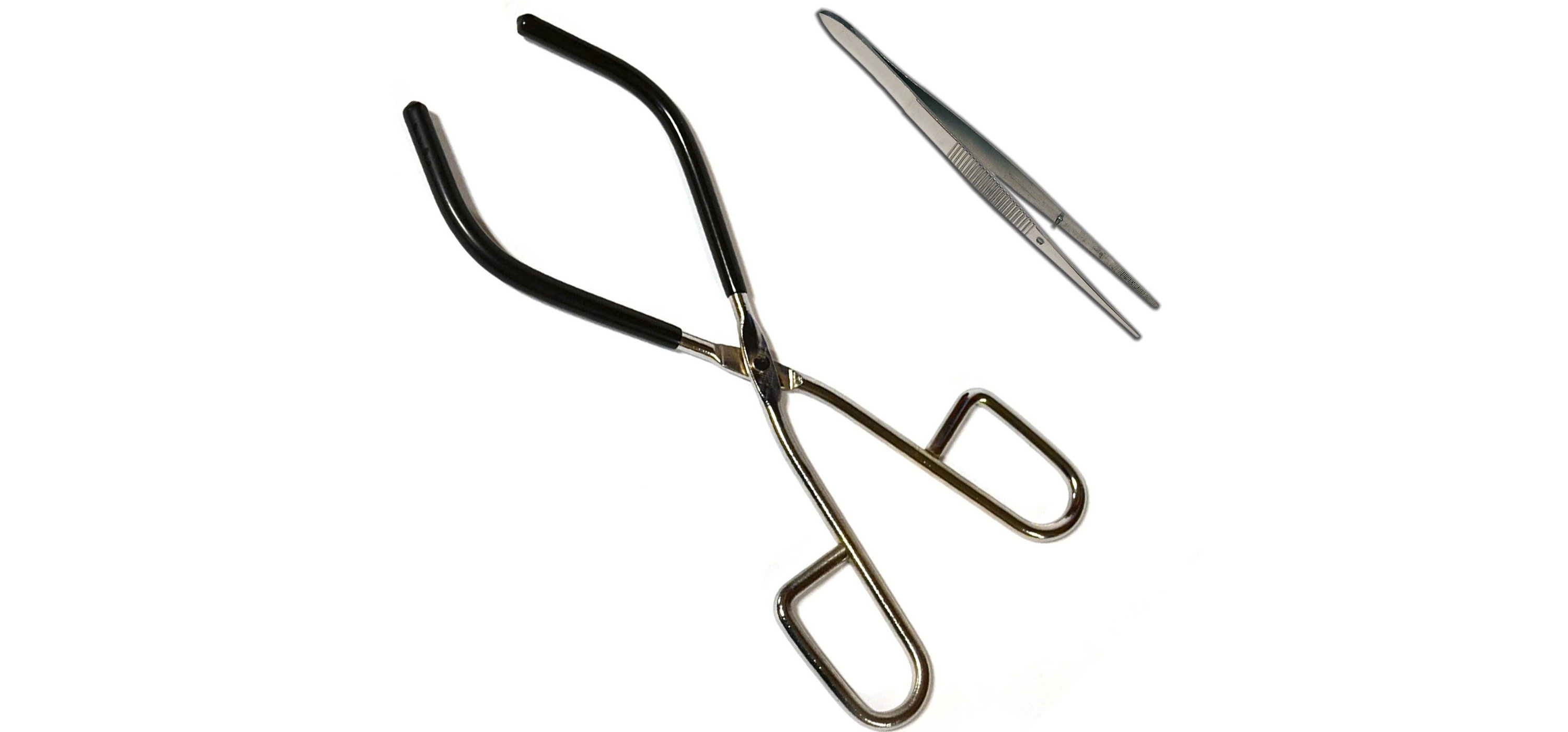
Tong and forceps are used for holding things that should not be touched by hand due to their size or heat. Apart from general purpose tongs, some are made to hold certain things like a beaker, test tubes etc. Forceps are used to grab small things like solid chemicals chunks, so they can be safely handled and added to containers.
SPATULA
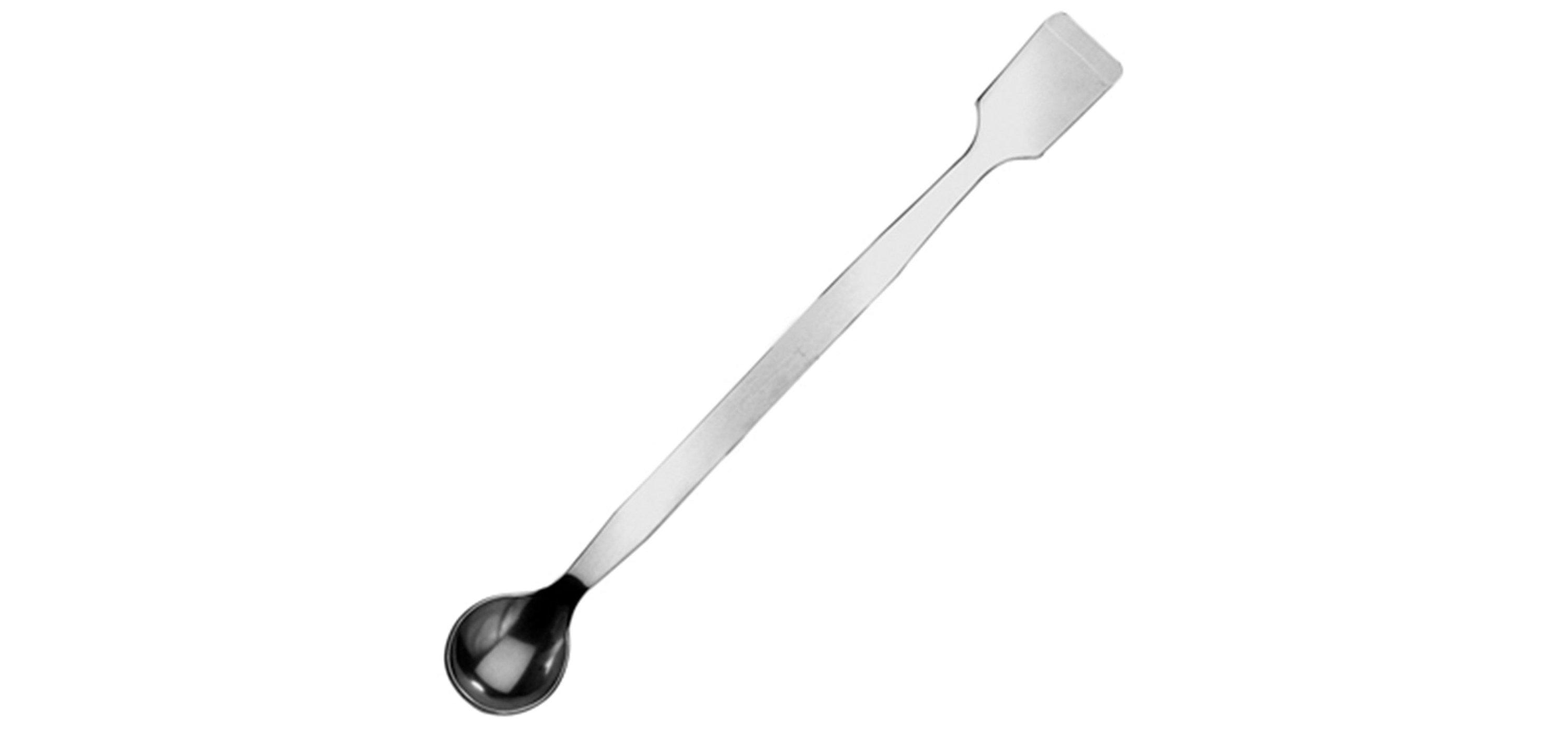

The spatula is like a spoon used for scooping solid chemicals. They are typically used to scoop a chemical out of its original container onto a weigh boat so that it can be weighed on a balance.
THERMOMETER
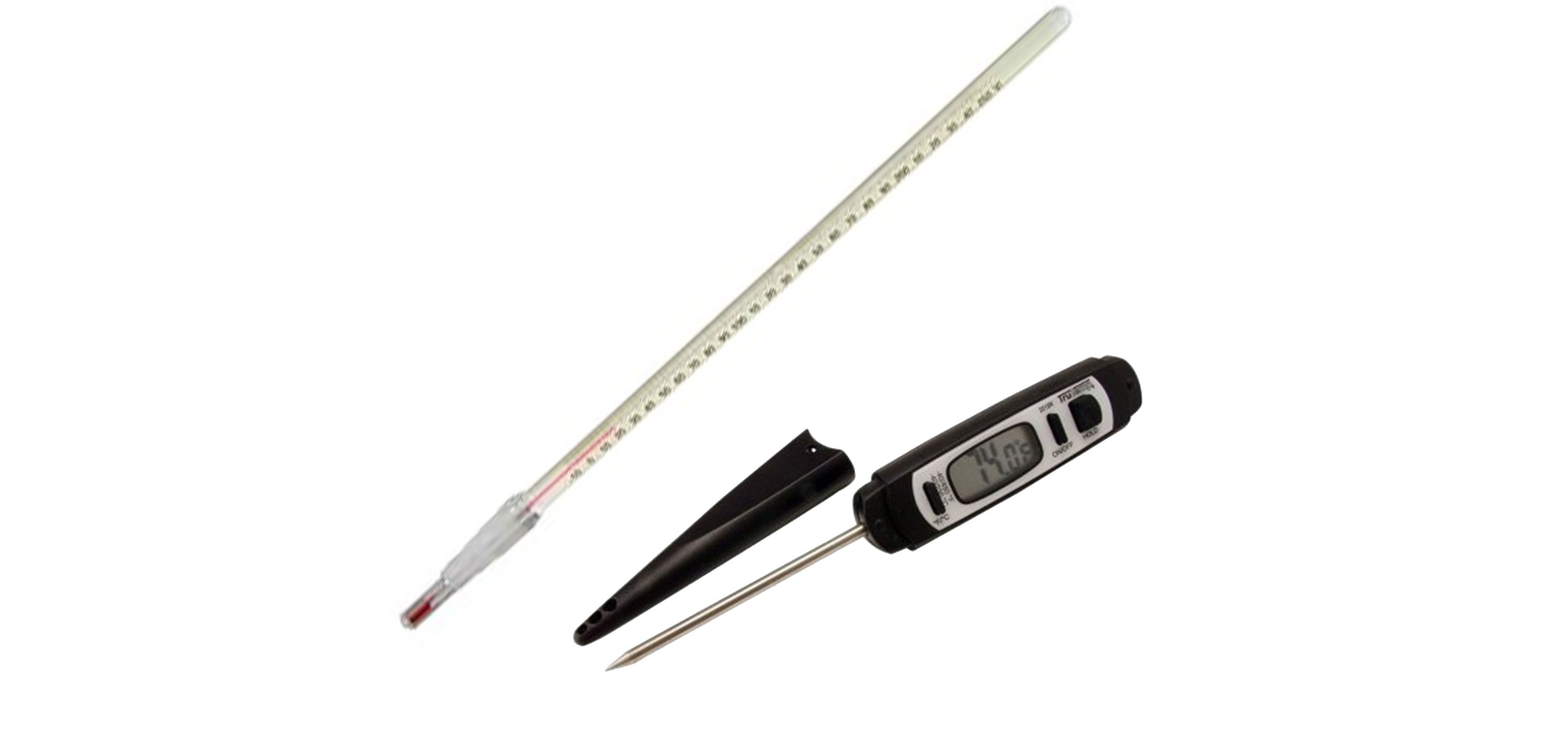
A laboratory thermometer is used for measuring precise temperature of liquids. It can be made of glass or it can be a thermocouple made of different metals. It is also available in digital and infrared model.
BUNSEN BURNER
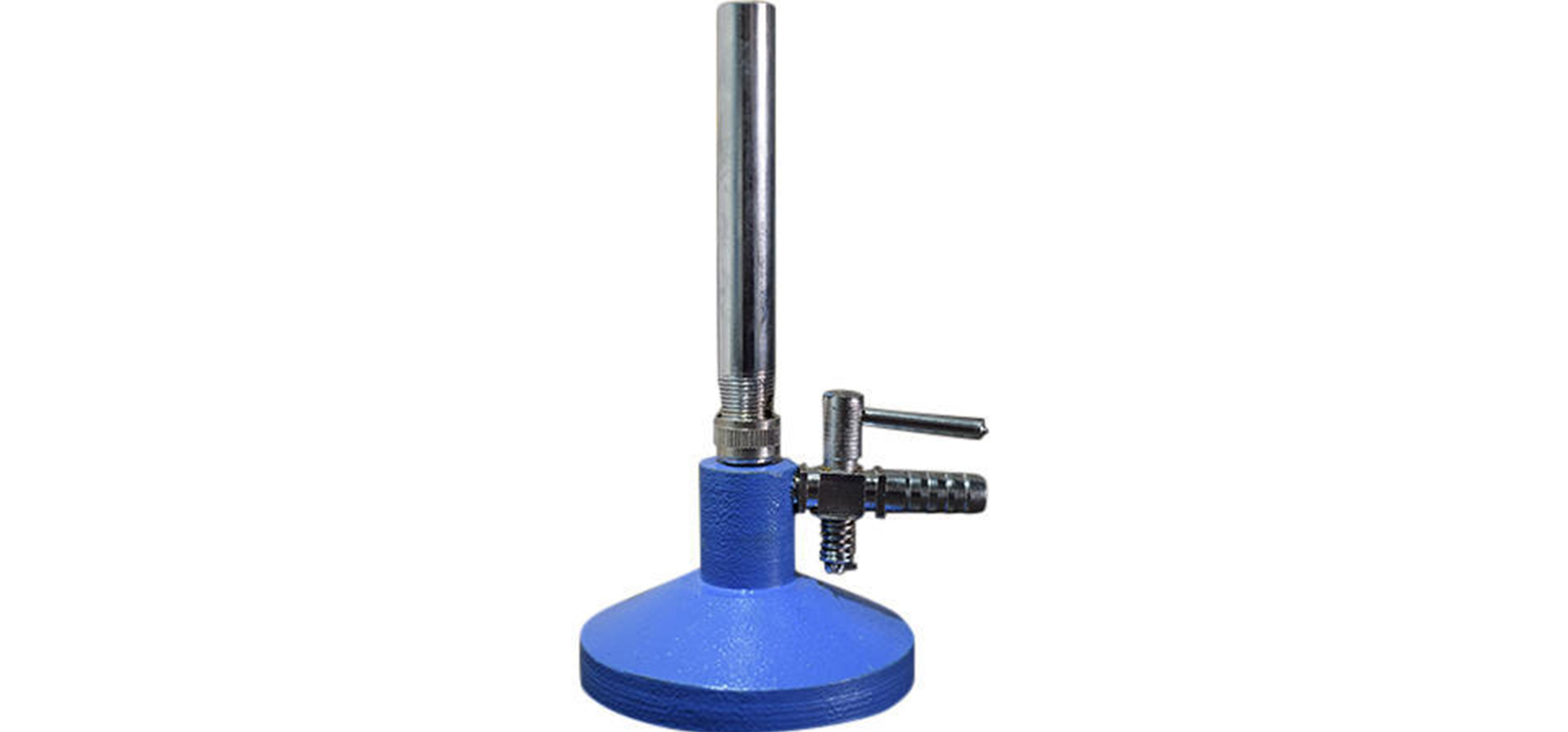

A Bunsen burner is a mechanical apparatus connected to a flammable gas source that produces a single open gas flame, which is used for heating, sterilization, and combustion. There is a knob to adjust the amount of gas flow and a rotating collar that controls airflow. These both must be adjusted to get an ideal flame for heating purposes. The burner is lit with a striker. The gas can be natural gas (which is mainly methane) or a liquefied petroleum gas, such as propane, butane, or a mixture of both.
BALANCE
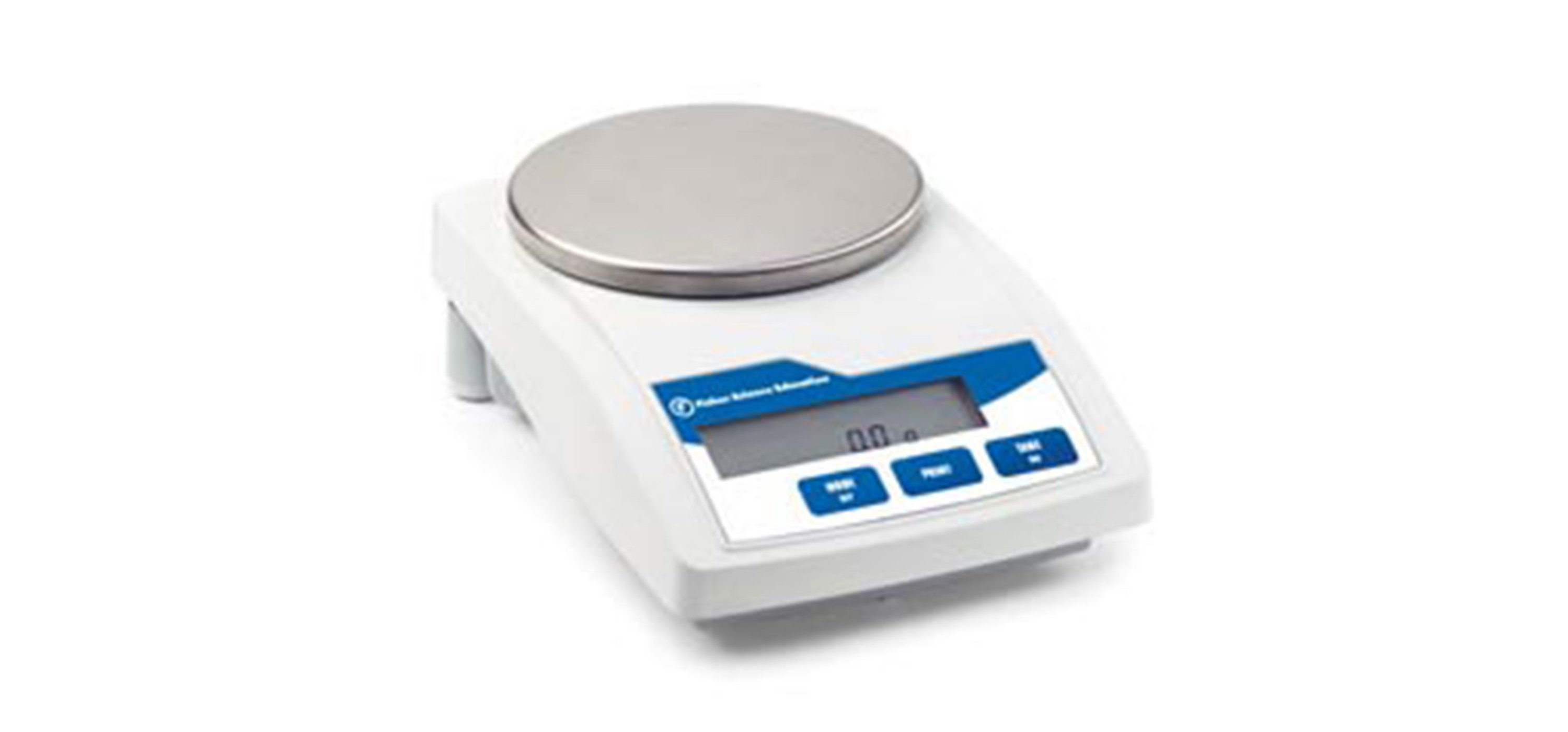

A balance is used to weigh chemicals. The chemicals are always in some container and to be never placed directly on the balance. It is important not to move a balance because they have been calibrated for the exact position they are in. To use a balance to determine the weight of a chemical, first put the empty container that the chemical will be in on the balance. Once you have a reading, press the “zero” button on the balance. Remove the container from the balance and add the chemical. Reweigh after adding the chemical to find the weight of only the chemical.
So, this was a brief overview of all the necessary items needed for your starting a chemistry laboratory from scratch.
At Labkafe, we provide laboratory furniture and equipment. In laboratory furniture, we first design entire laboratory room keeping in mind the requirements. Also, we take care of complete installation of laboratory furniture. In lab equipment section, we have a wide range of glassware, chemicals, equipment and other lab accessories. Most of them are available for order online from our website but some of them can be procured on demand. If you have any sort of laboratory requirements do WhatsApp us or mail us at [email protected] and we’ll get in touch with you.












Leave a Reply