Ever performed a titration in the lab only to find an absurd value? The process of reloading the burette might sound scary, but what’s worse is the fact that the analyte in your flask is now ruined. Even though the color in your flask isn’t what it should be, the volume you need has already been dispensed from the burette. So now what to do? How did this happen? This is your chemistry lab burette’s fault. Read along to find out how you can avoid this from happening to you ever again, by choosing the right chemistry lab burettes.
What is a chemistry lab burette?
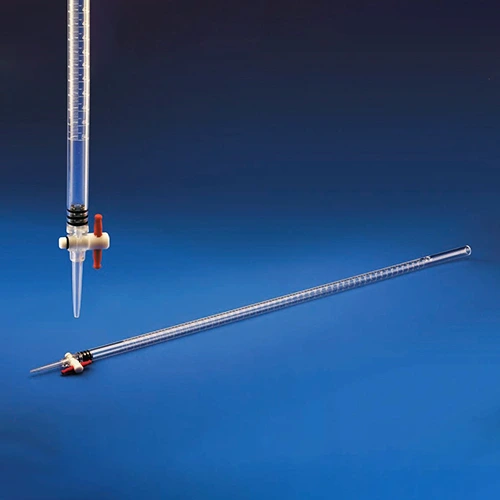

Chemistry lab burettes help dispense exact amounts of reagents drop by drop or in a stream. They are used for experiments in the school lab or for research in chemistry. Invented by François Antoine Henri Descroizilles in 1791, the burette was later refined by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac.
What are the uses of a chemistry lab burette?
It helps researchers and students dispense exact proportions of liquids and gases, thereby helping determine the concentration of unknown solutions.
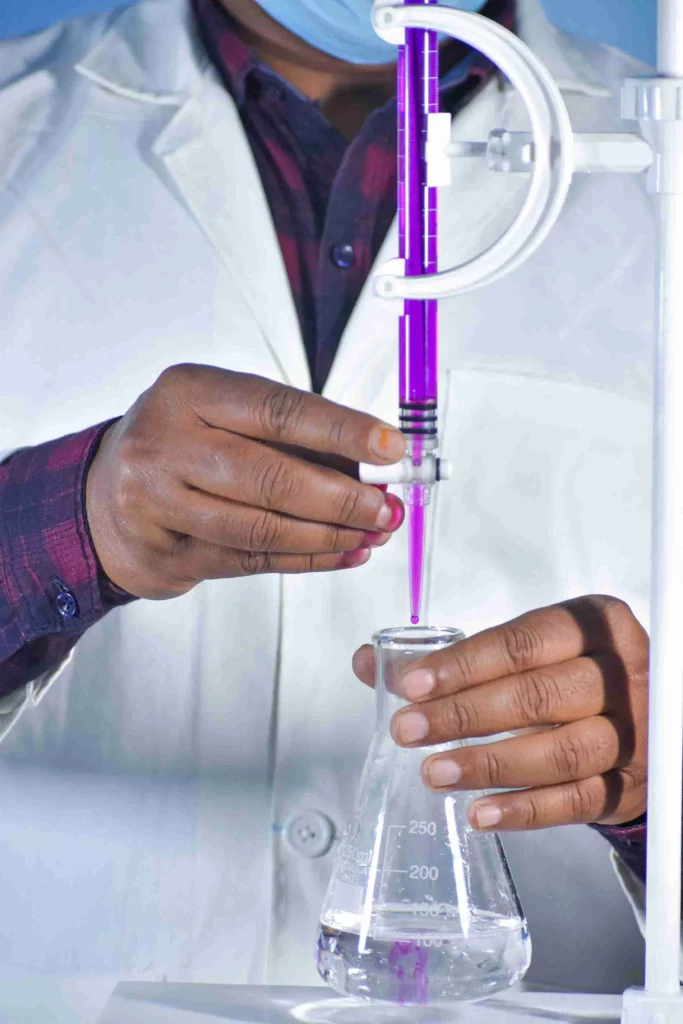
One solution is tested against another. The burette contains the titrant, and the flask has the analyte with unknown concentration. The titrant is titrated from the burette against the analyte. This helps determine the concentration of the analyte in the flask.
Types of chemistry lab burettes
Different types of burettes exist that help users perform different types of operations and experiments. Each type is optimised for a specific range of operations and must not be misused for others.
Classification by mechanism of operation
Volumetric burette

The volume scale is printed on the burette wall. There is a plastic stopcock at the bottom that needs to be opened or closed in order to dispense the fluid. Gravity helps the liquid flow downwards. Because the opening is at the bottom of the burette, the level change is noted and corresponds to the amount of fluid dispensed. This is a manual burette, as it is handled by a human. The stopcock or valve is operated manually. It does not have a digital or electronic variant.
How to use a volumetric burette?
- Rinse burette with the titrant to be used.
- Rotate to coat the inner surface evenly with titrant.
- Drain excess titrant through stopcock into waste beaker.
- Clamp burette securely to the stand.
- Fill with titrant.
- Note initial volume using the lower meniscus.
- Open the stopcock slowly to release the titrant into the analyte in the conical flask.
- Continue until the desired amount is released.
- Note final volume in the burette.
- Calculate volume delivered (initial – final).
- Drain and rinse burette with water.
- Store safely.
Piston burette
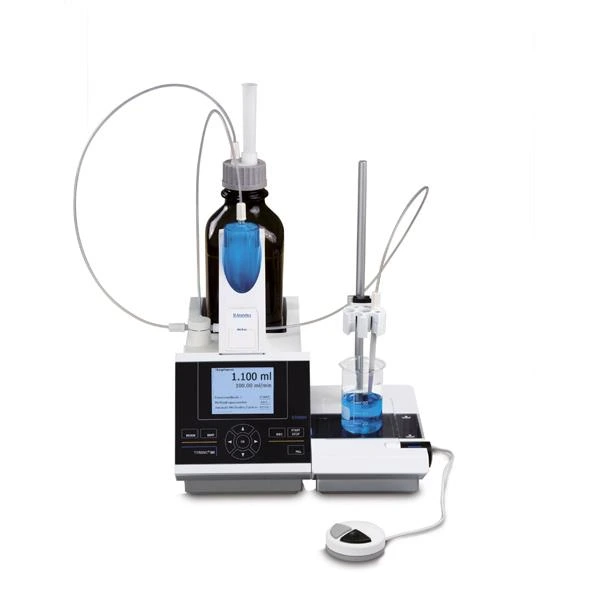

This has a syringe design with a barrel and plunger arrangement. The barrel dispenses the fluid. The barrel is always fixed in position. The plunger is moved slowly using a dial that is rotated. The rotation moves the plunger and releases the titrant from the barrel.
The measurements are extremely precise—more than that of the volumetric burette—and the amount dispensed is shown on a digital monitor at the top of the burette.
This is hence called a digital burette, as the basic version is always digital, meaning the plunger is never operated manually. It is always operated by incremental movement of the dial.
Further advanced variations of this are called electronic burettes, which allow precise measurements and are the most accurate chemistry lab burettes. The entire dispensing mechanism is computerised, meaning the knob or dial is not operated by hand anymore. Because a computerized system is used, highly precise and accurate amounts of the titrant are dispensed, eliminating chances of human error. Hence, it gives trustworthy results.
How to use an electronic piston burette?
- Insert batteries into the control unit and close the panel.
- Connect cable from burette to control panel.
- Attach a telescopic tube to the base of the burette.
- Fix adapter suitable for the reservoir bottle.
- Mount burette on the reservoir and tighten gently.
- Charge if needed using the power cable.
- Switch on the control panel.
- Turn knob to recirculation when prompted on screen.
- Purge the burette to remove air bubbles.
- Repeat purge if air bubbles remain.
- Select titration mode from the control panel.
- Turn knob to titration and confirm on screen.
- Place the tube in the vessel for accurate delivery.
- Fill the barrel by clicking the fill button.
- Dispense titrant using desired speed mode.
- Press TARE to reset volume to zero.
- Repeat dispensing as required for titration.
Classification by type of fluid handled
Liquid burette
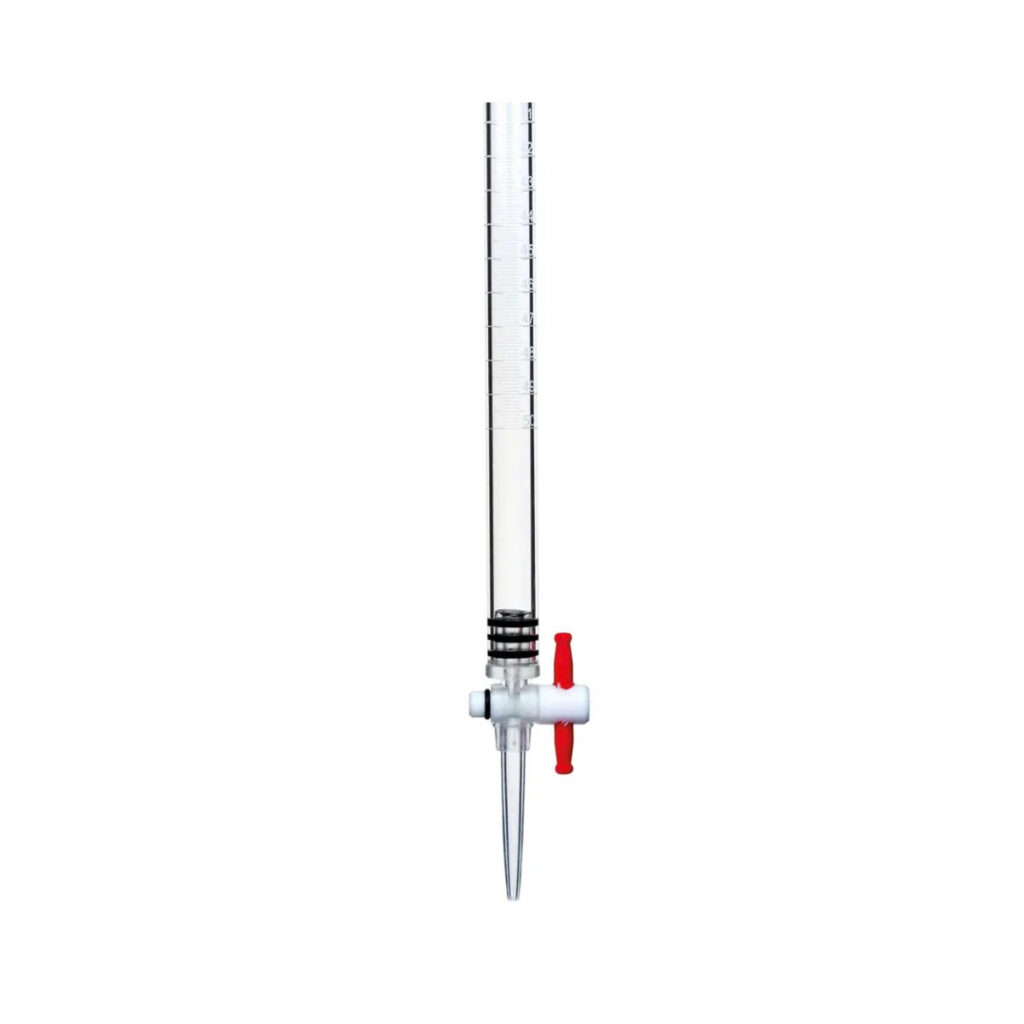

Dispenses liquids. The stopcock is at the bottom of the burette, and the flow of fluid is enabled by gravity. The wall of the burette has graduation marks which show how much of the liquid has flowed through the burette.
Gas burette
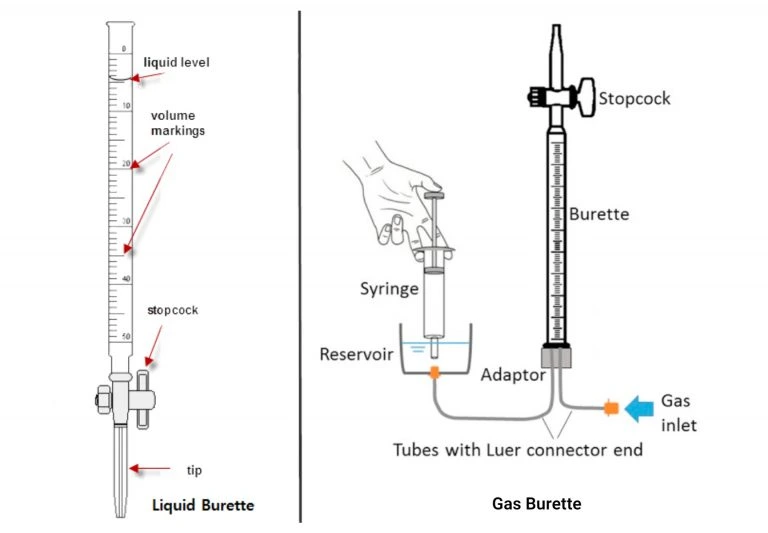
Dispenses gases. In a gas burette, the stopcock is at the top. The tube of the burette is filled with a fluid, such as water, oil, or mercury, and the bottom of the tube is attached to a reservoir of the same fluid. Gas is collected by displacing fluid from the burette, and the amount of gas is measured by the volume of fluid displaced from the burette.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is burette in a laboratory?
A chemistry lab burette is an instrument used to dispense exact proportions of reagents drop by drop or in a stream during school experiments or research in chemistry.
Which is the correct spelling, buret or burette?
Burette is UK English; buret is US English. Both are correct. Maintain the same usage throughout the literature that you’re writing.
What are the different types of chemistry lab burettes?
There are two main types of chemistry lab burettes: volumetric and piston. Volumetric burettes are operated manually and use gravity to dispense liquid. Piston burettes are more precise and are operated digitally or electronically, often through automated systems. They are more accurate than volumetric burettes.
What are 2 uses of lab burette in chemistry?
- Titration – To find the concentration of an unknown solution by reacting it with a titrant of known concentration.
- Sample preparation – To mix specific volumes of liquids for accurate sample creation in analytical experiments.
What is the difference between liquid burette and gas burette?
- A liquid burette dispenses liquids using gravity, with a stopcock at the bottom.
- A gas burette collects gases by displacing liquid from the tube, with a stopcock at the top. The amount of gas is measured by the volume of liquid displaced from the burette.












Leave a Reply